Stock Trading For Beginners



Trading in stocks is an exciting market for beginners and established investors. This guide will cover which stocks to look for when aiming for short-term positions to buy or sell (ideally you need highly liquid, and volatile stocks).
You will learn how to pick stocks and when to trade them, as well as trading strategies that could help you find trades. We also list where to buy stocks right now.
Quick Introduction
- Stock trading involves buying and selling company shares listed on stock exchanges to profit from price changes.
- Traders generally try to buy shares when the price is low and then sell them when the price is high, profiting from the difference (minus any fees).
- Shares can often be bought and sold directly at stock brokers. However, they can also be traded using derivatives like CFDs, which allow traders to speculate on rising and falling prices without owning the underlying stock.
- While stocks are often thought of as long-term investments, stock trading also appeals to day traders with an effective strategy.
- The ability to short prices, or trade on company news and events, means short-term trades can provide opportunities.
Best 4 Stock Trading Brokers
These brokers offer the best stock trading service, including exposure to a wide range of companies, sectors and regions, plus low fees and excellent market research:
Latest Stock Trading Posts
Download DayTrading.com’s Stock Trading For Beginners PDF
What Is Stock Trading?
Stock trading is the practice of buying and selling financial instruments known as stocks or shares, which represent ownership in publicly traded companies. These transactions occur within financial markets, where investors and traders seek to capitalize on price fluctuations to generate returns.
The fundamental principle underlying stock trading revolves around the pursuit of capitalizing on discrepancies between the buying and selling prices of stocks.
Market participants engage in stock trading for various reasons, including the potential for capital appreciation, dividend income, or hedging against other investment positions. Traders analyze market trends, company financials, industry dynamics, and macroeconomic indicators to inform their decisions.
Different trading strategies are employed, such as day trading, swing trading, and long-term trading, each carrying distinct levels of risk and potential reward.
It is crucial to note that stock trading necessitates a comprehensive understanding of market mechanisms, risk management, and financial analysis, as the endeavor entails exposure to market volatility and economic shifts.
Stock Trading Vs Investing
Stock trading and investing are distinct approaches, each characterized by unique strategies, objectives, and time horizons. Understanding the differences between the two is important.
Stock Trading
Stock trading involves the frequent buying and selling of stocks or other financial instruments with the primary goal of capitalizing on short-term price fluctuations. Traders often use technical analysis, charts, and market trends to make quick and tactical decisions.
Here are the key points that differentiate stock trading:
- Time Horizon: Stock trading typically has a short-term time horizon, ranging from minutes to weeks. Traders seek to profit from quick price movements.
- Frequency: Traders can engage in multiple trades within a single day (day trading) or hold positions for a few days to weeks (swing trading).
- Focus: Stock trading emphasizes taking advantage of market inefficiencies, price patterns, and short-term trends to generate profits.
- Risk and Reward: The potential for high returns exists due to frequent trading, but it comes with elevated risk due to market volatility and transaction costs.
- Involvement: Active monitoring of the markets, rapid decision-making, and continuous research are necessary for successful stock trading.
Stock Investing
Stock investing, on the other hand, revolves around buying and holding stocks for the long term with the goal of achieving steady growth and potential dividend income.
Here are the distinguishing characteristics of stock investing:
- Time Horizon: Investing entails a longer time horizon, typically ranging from several months to years. The focus is on the company’s fundamentals and long-term growth potential.
- Patience: Investors rely on fundamental analysis, company financials, industry trends, and economic outlook to make informed decisions. They are less concerned with short-term market fluctuations.
- Risk and Reward: Investing seeks to capitalize on the overall growth of a company and the economy. While potentially offering more stable returns, the pace of growth may be slower compared to stock trading.
- Involvement: Stock investors don’t require constant monitoring and trading activity. Instead, they emphasize a buy-and-hold approach, allowing time for their investments to appreciate.
- Dividend Income: Investors often prioritize companies that offer consistent dividend payments as a source of income in addition to potential capital appreciation.
Ultimately, stock trading is centered on exploiting short-term market movements for quick gains, while stock investing involves a patient, long-term approach focused on steady growth and potential income.
The choice between trading and investing depends on your individual goals, risk tolerance, time availability, and expertise in market analysis.
Types Of Stocks You Can Trade
Various types of stocks are available for trading, each characterized by specific attributes and characteristics.
Common stock is the most prevalent form, representing ownership in a company and entitling shareholders to voting rights and potential dividends.
Preferred stock, on the other hand, offers priority dividend distributions and potentially greater claim in case of liquidation but typically lacks voting rights.
Furthermore, stocks are categorized based on market capitalization:
- Large-Cap Stocks: A large-cap stock refers to a company with a significant market capitalization, typically exceeding several billion dollars, indicating its established presence and prominence within the financial markets.
- Mid-Cap Stocks: A mid-cap stock refers to a company with a market capitalization between that of large-cap and small-cap stocks, indicating a moderate level of size and potential for growth within the financial markets.
- Small-Cap Stocks: A small-cap stock refers to a company with a relatively small market capitalization, generally ranging from a few hundred million to a couple of billion dollars, often associated with higher growth potential and increased volatility within the financial markets.
- Penny Stocks: A penny stock is a term often used to describe low-priced stocks that trade at a relatively low market price, typically below $1 per share, and are often associated with smaller, less established companies and higher trading risks.
- Growth Stocks: A growth stock is a type of stock issued by a company that is expected to grow its earnings and revenues at an above-average rate compared to other companies in the market, often leading to potential capital appreciation over time.
- Value Stocks: A value stock is a stock that is considered undervalued by investors based on fundamental analysis, often trading at a lower price compared to its intrinsic worth, with the potential for price appreciation as market perception aligns with its true value.
- Income Stocks: An income stock is a type of stock known for providing regular dividends to its shareholders, offering a steady income stream in addition to the potential for capital appreciation.
What Affects Stock Prices?
Stock prices are subject to a complex interplay of factors that collectively shape their movement within financial markets. These influences encompass both internal dynamics specific to the company and external market forces.

Here’s more detail on the key factors that influence stock prices:
- Company Performance: Earnings reports, revenue growth, profit margins, and other financial metrics directly affect investor perception of a company’s health and future prospects, consequently influencing stock prices.
- Economic Indicators: Broader economic indicators such as GDP growth, inflation rates, and unemployment levels can impact investor sentiment and subsequently influence stock market movements.
- Market Sentiment: Investor perception of market conditions, geopolitical events, and macroeconomic trends contribute to market sentiment, which can drive buying or selling activity.
- Interest Rates: Central bank decisions on interest rates influence borrowing costs, affecting both consumer spending and corporate profitability, ultimately impacting stock valuations.
- Industry Trends: Sector-specific dynamics, technological advancements, and regulatory changes within industries can significantly influence stock prices.
- Company News: Positive or negative news, such as product launches, regulatory approvals, lawsuits, or management changes, can cause sudden price fluctuations.
- Market Speculation: Investor speculation and sentiment-driven trading can create short-term price volatility.
- Market Supply And Demand: Basic supply and demand dynamics determine the equilibrium price of a stock. Increased demand relative to supply can drive prices up, and vice versa.
- Earnings Expectations: Stock prices are influenced by how a company’s actual earnings compare to market expectations.
- Dividend Payments: Companies that offer dividends can attract income-seeking investors, potentially affecting demand and stock price.
- Global Events: Political instability, international conflicts, and natural disasters can lead to market uncertainty and impact stock prices.
- Currency Fluctuations: For international companies, changes in exchange rates can affect their earnings and subsequently influence stock prices.
- Regulatory Environment: Changes in regulations, tax policies, or government interventions can impact a company’s profitability and influence stock prices.
- Market Liquidity: Thin trading volumes can lead to greater price volatility, as large trades can have a more pronounced impact on prices.
- Technical Factors: Chart patterns, moving averages, and other technical indicators are used by traders to make buy or sell decisions, contributing to short-term price movements.
It is important to note that stock prices are the result of the collective interpretation of these diverse factors by market participants. Consequently, understanding and assessing these influences is vital in order for you to make informed investment decisions.
How To Trade Stocks
The best day trading stocks provide you with opportunities through price movements and an abundance of shares being traded.
This will enable you to enter and exit those opportunities swiftly. These factors are known as volatility and volume. You may be thinking ‘I’ve heard of day trading volatile stocks and volume before, but what does that really mean?’
Volume
Volume is concerned simply with the total number of shares traded in a security or market during a specific period. Each transaction contributes to the total volume. If just twenty transactions were made that day, the volume for that day would be twenty.
How is that used by a day trader making his stock picks? Volume acts as an indicator giving weight to a market move. If there is a sudden spike, the strength of that movement is dependent on the volume during that time period.
Put simply, the greater the volume, the more significant the move.
Using Volume
If you have substantial capital behind you, you need stocks with significant volume. Whilst your brokerage account will likely provide you with a list of the top 20-25 stocks, one of the best day trading stocks tips is to broaden your search a little wider.
That way you can find opportunities that aren’t on every other trader’s radar. Look for stocks with a spike in volume.
If a stock usually trades 2.5 million shares daily, but you notice it has traded 6 million shares by 10 am, then this could be worth exploring. If your chosen platform fails to offer a rigorous screener for high-volume stocks, utilize these alternatives:
- Bar Chart
- TheStreet
- Yahoo Finance Unusual Volume
Volatility
Volatility is concerned with the amount of risk/unpredictability in the size of changes in a security’s value. If it has a high volatility the value could be spread over a large range of values.
Ideally, short-term trades require volatile stocks.
This would mean the price of the security could change drastically in a short space of time, making it ideal for the fast-moving day trader.
Whereas if it has low volatility, the security’s value will remain relatively steady, offering less opportunity for a quick trade opportunity.
Beta
One way to establish the volatility of a particular stock is to use beta. The beta predicts the total volatility of a security’s returns against the returns of an appropriate benchmark (normally the S&P 500).
A stock with a beta value of 1.2 has moved approximately 120% for every 100% in the benchmark, contingent on the price level. On the flip side, a stock with a beta of just .8 has moved 80% for every 100% in the comparative index.
How To Find Stocks To Day Trade
So finding the best stocks to day trade is a matter of searching for assets with large volume, or a recent spike in volume, and a beta higher than 1.0 (the higher the better – a more volatile stock).
Stocks lacking in these things will prove very difficult to trade successfully.
How you use these factors will impact your trading choices, and will depend on your strategies for day trading stocks. Profiting from a price that does not change is impossible.
Buyers and sellers create price movement, a lack of volume shows a lack of buyers and sellers.
Defensive stocks, while normally associated with lower volatility, may suddenly be in demand if a market panic causes a flight to safer investments, so volume and volatility may not always spring up in the obvious places.
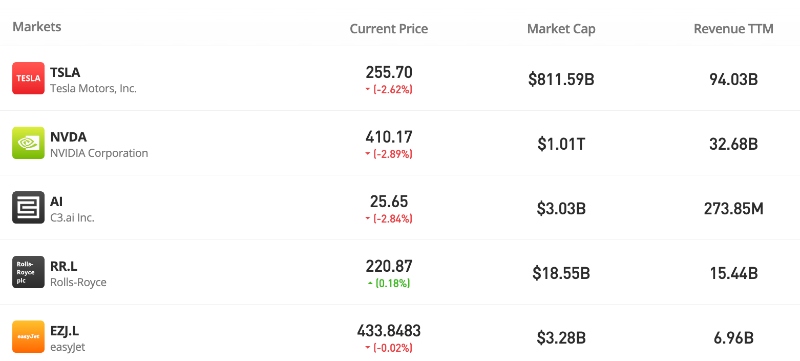
Best Day Trading Stocks 2026
Now you have an idea of what to look for in a stock and where to find them. Below is a breakdown of some of the most popular day trading stock picks.
With volume being such an important element for finding the top stocks to day trade, it is no surprise that the US market is where the better stock choices are to be found today:
US Stocks
| Stock | Symbol | Strength | Trade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apple | APPL | Volume | |
| Meta | META | Volume+Volatility | |
| Microsoft | MSFT | Volume | |
| Ford | F | Volume | |
| Tesla | TSLA | Volatility | |
| Google (Alphabet) | GOOG | Volume+Volatility | |
| S and P | US 500 | Volume+Volatility |
In the UK, the stocks boasting the highest volume offer the best day trading opportunities
UK Stocks
| Stock | Symbol | Strength | Trade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barclays | BARC | Volume+Volatility | |
| Lloyds Bank | LLOY | Volume+Volatility | |
| Vodafone | VOD | Volume | |
| BP | BP | Volume |
The UK can often see a high beta (volatility) across a whole sector. House builders, for example, all saw an increased beta figure in recent years, driven in part by the fears over any Brexit impact.
Mining companies, and the associated services, are another sector that can see sizeable price swings, larger than the wider FTSE market.
Each trading approach comes with its own advantages, risks, and suitability depending on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and level of expertise. It is important to thoroughly understand these methods before engaging in any trading activity.
How Stock Market Trading Times Affect Trading Strategies
Stock market trading times can significantly impact your trading strategy due to the availability of liquidity, volatility, and market participants during different sessions. Here’s how:
- Regular Trading Hours: The main trading hours are when markets are most active and have the highest liquidity. This is when most institutional investors and traders are active, leading to tighter bid-ask spreads and smoother execution of trades. Strategies that rely on quick price movements, such as day trading and short-term momentum trading, are more effective during these hours due to increased trading volumes and price volatility.
- Pre-Market And After-Hours Trading: These extended-hours sessions offer opportunities for traders to react to news releases and corporate earnings announcements that occur outside regular trading hours. However, liquidity during these times is often lower, leading to wider bid-ask spreads and potentially more significant price gaps. Traders employing these sessions should be cautious of the increased risk.
- International Markets Overlaps: When multiple major markets overlap, such as the opening of the New York and London markets, there can be heightened volatility and increased trading activity as participants from different regions interact. Strategies focusing on currency pairs, global macroeconomic events, and cross-market correlations can benefit from these overlaps.
- Time Zone Considerations: Traders in different time zones need to adjust their strategies to align with the market hours they have access to. For example, a trader in Asia might engage in strategies that take advantage of the opening hours of Asian markets.
- Market Closures And Holidays: Market closures due to holidays can lead to gaps in trading activity and changes in market sentiment upon reopening. Traders should be aware of upcoming holidays in relevant markets to adjust their positions or strategies accordingly.
- Earnings Announcements And Economic Data Releases: Many trading strategies involve reacting to earnings reports, economic indicators, and news releases. Traders need to be aware of the timing of these events, as they can lead to increased volatility and potential trading opportunities.
In essence, you need to align your strategies with the specific trading hours you intend to participate in and consider the liquidity, volatility, and participant behavior during those times.
Different strategies thrive under different market conditions, and understanding how trading times influence these conditions is vital for successful execution.
How to Figure Out Target Prices
1. Define the type of trade
- Investor-style target: months/years out → use P/E or DCF.
- Trader-style target: days/weeks → use ATR + key levels.
2. Get a valuation anchor (P/E or DCF)
- P/E method: estimate next year’s EPS → pick a realistic P/E (based on sector/peers, not the most optimistic) →
Target = EPS × P/E. - DCF method: project cash flows with conservative growth assumptions → discount them back → divide by shares to get a fair value per share.
- This gives you a long-term fair value range, especially useful for growth names.
3. Layer on ATR for realistic movement
- Check the stock’s ATR (e.g. daily ATR = $2).
- From your planned entry, set near-term targets at about 1–2× ATR in your direction (e.g. buy at $50 → short-term targets $52, $54).
- This keeps targets in line with how much the stock actually moves.
4. Align targets with levels and volatility
- Only use an ATR-based target if it lines up with support/resistance or other technicals (e.g. don’t set a $54 target if there’s a clear resistance at $53).
- In high volatility (ATR rising), allow wider targets and stops; in low volatility, keep them tighter.
5. Set exits and review
- Use ATR for stop-loss/trailing stops (e.g. 1–1.5× ATR away).
- As earnings, news, or cash-flow assumptions change, recalculate your valuation anchor (P/E or DCF) and adjust your short-term ATR targets around it.
Bottom Line
Trading in stocks can be a rewarding but complex venture. It involves buying and selling shares of publicly traded companies in financial markets.
To excel in stock trading, you must develop a sound strategy, grounded in thorough research and analysis. This might include studying market trends, company fundamentals, and economic indicators to make informed decisions.
However, it is key to remember that stock trading carries inherent risks due to market volatility and unpredictability. Therefore, prudent risk management, diversification of investments, and a clear understanding of your financial goals and risk tolerance are essential.
Successful stock trading often requires continuous learning, discipline, and the ability to adapt to changing market conditions.
Stock Exchanges
- Abu Dhabi Securities Exchange Brokers 2026
- Australian Securities Exchange (ASX) Brokers 2026
- Bombay Stock Exchange Brokers 2026
- Borsa Italiana Brokers 2026
- CAC 40 Index France Brokers 2026
- Chicago Mercantile Exchange Brokers 2026
- DAX GER 40 Index Brokers 2026
- Deutsche Boerse Brokers 2026
- Dow Jones Brokers 2026
- Dubai Financial Market Brokers 2026
- Euronext Brokers 2026
- FTSE UK Index Brokers 2026
- Hang Seng Brokers 2026
- Hong Kong Stock Exchange Brokers 2026
- IBEX 35 Brokers 2026
- Japan Exchange Group Brokers 2026
- Korean Stock Exchange Brokers 2026
- London Metal Exchange Brokers 2026
- London Stock Exchange Brokers 2026
- Nairobi Securities Exchange Brokers 2026
- Nasdaq Brokers 2026
- Nasdaq Dubai Brokers 2026
- Nasdaq Nordic & Baltics Brokers 2026
- National Stock Exchange Of India Brokers 2026
- New York Stock Exchange Brokers 2026
- Russell 2000 Brokers 2026
- S&P 500 Brokers 2026
- Shanghai Stock Exchange Brokers 2026
- Shenzhen Stock Exchange Brokers 2026
- SIX Swiss Exchange Brokers 2026
- Tadawul Brokers 2026
- Taiwan Stock Exchange Brokers 2026
- Tokyo Commodity Exchange Brokers 2026
- Toronto Stock Exchange Brokers 2026
Specific Stock Trading Tutorials
FAQ
Why Day Trade Stocks?
Day trading stocks today is dynamic. On top of that, they are not complex to buy and sell, and in the world of technology, the market is readily accessible.
The liquidity in markets means speculating on prices going up or down in the short term is viable. Also, stocks are relatively straightforward to understand and follow.
Whilst day trading in the complex technical world of cryptocurrencies or forex may leave you scratching your head, you can get to grips with the triumphs and potential pitfalls of Google and Facebook more easily.
This means identifying which stocks suit online trading intraday hopefully won’t be as challenging as it is in other markets.
When Can You Trade The Stock Markets?
The major stock market trading times are as follows. However, bear in mind that these times may be affected by daylight saving time changes, holidays, and other factors.
Additionally, some markets offer pre-market and after-hours trading sessions that allow for trading outside of regular hours. It is important to verify the specific trading hours of the market you’re interested in to ensure accuracy.
- New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and NASDAQ: These markets in the United States operate from 9:30 AM to 4:00 PM Eastern Time (ET), Monday through Friday, with pre-market and after-hours trading sessions.
- London Stock Exchange (LSE): The LSE operates from 8:00 AM to 4:30 PM Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), Monday through Friday.
- Tokyo Stock Exchange (TSE): The TSE operates from 9:00 AM to 3:00 PM Japan Standard Time (JST), Monday through Friday.
- Hong Kong Stock Exchange (HKEX): The HKEX operates from 9:30 AM to 4:00 PM Hong Kong Time (HKT), Monday through Friday.
- Frankfurt Stock Exchange (FSE): The FSE operates from 9:00 AM to 5:30 PM Central European Time (CET), Monday through Friday.
What Are The Most Popular Stock Trading Strategies?
Stock trading offers a spectrum of strategies and methods for you to engage with financial markets. Here are the different ways you can trade stocks:
- Scalping: Traders aim to profit from small price movements by making frequent and rapid trades, often holding positions for just seconds to a few minutes.
- Day Trading: Involves executing multiple trades within a single trading day, capitalizing on intraday price movements.
- Swing Trading: Traders hold positions for a few days to weeks, aiming to profit from short- to medium-term price fluctuations.
- Position Trading: Longer-term approach where positions are held for several weeks to months, based on fundamental analysis and macroeconomic trends.
- Long-Term Investing: Holding stocks for an extended period, often years, focusing on company fundamentals and growth potential.
- Value Investing: Seeking undervalued stocks trading below their intrinsic value, with potential for future appreciation.
- Growth Investing: Targeting companies with high growth potential, often reinvesting profits into expanding operations.
- Dividend Investing: Focusing on stocks with a history of regular dividend payments to generate consistent income.
What Is The Difference Between Stocks, Mutual Funds and ETFs?
Stocks, mutual funds, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are all investment vehicles, but they differ in how they are structured and traded.
Stocks represent ownership in a specific company. When you buy a stock, you own a share of that company. You trade individual company shares on stock exchanges, and prices are determined by market supply and demand. Trading individual stocks can involve more research and decision-making on specific companies.
Mutual funds are investment vehicles that pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. When you invest in a mutual fund, you buy shares of the fund itself, not individual stocks. Mutual funds are typically managed by professional fund managers who make investment decisions on behalf of the investors. Mutual funds are traded at the end of the trading day at their net asset value (NAV) price, which is calculated based on the value of the underlying assets. Mutual funds are better suited for long-term investors who don’t need real-time trading.
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are similar to mutual funds in that they also pool money from investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of assets. However, ETFs are traded on stock exchanges, just like individual stocks. This means you can buy and sell ETF shares throughout the trading day at market prices, and their prices can fluctuate like stocks. ETFs often aim to track the performance of an underlying index or asset class, and they offer the diversification benefits of a mutual fund with the flexibility of stock-like trading. ETFs are suitable for both long-term investors and traders looking for short-term opportunities.
The choice between these trading options depends on your goals, risk tolerance, and preferences. Long-term investors often find mutual funds and ETFs more suitable for diversification, while those looking for active trading opportunities may prefer individual stocks or ETFs.
Recommended Reading
Article Sources
- A Beginner’s Guide To The Stock Market: Everything You Need to Start Making Money Today - Matthew R Kratter, 2019
- Online Trading and Stock Investing for Beginners: The Easy Way To Start Trading and Getting Rich In The Stock Market - Michael Wells Instafo, 2019
- Penny Stocks Investing For Beginners: Penny Stock Trading Guide - Robert Alderman, 2014
- The Big Book Of Stock Trading Strategies - Matthew R Kratter, 2017
- Trading Basics: Understanding The Different Ways To Buy & Sell Stock - SEC
- LSE Issuers - London Stock Exchange
The writing and editorial team at DayTrading.com use credible sources to support their work. These include government agencies, white papers, research institutes, and engagement with industry professionals. Content is written free from bias and is fact-checked where appropriate. Learn more about why you can trust DayTrading.com