Kinetic Exchange Models of Markets – Applications in Finance & Markets

Kinetic exchange models are a tool for understanding the complex dynamics of financial markets.
These models, rooted in the kinetic theory of statistical physics, offer a unique econo-physical perspective on the movement of money, credit, and assets within a market.
By leveraging the principles of statistical physics, financial researchers and analysts can gain a deeper understanding of market behaviors, trends, and potential future movements.
Key Takeaways – Kinetic Exchange Models of Markets
- Kinetic Exchange Models in Finance: Kinetic exchange models, inspired by the kinetic theory of statistical physics, provide a unique approach to understanding the movement of money, credit, and asset prices.
- These models leverage probabilistic and statistical methods to gain insights into market dynamics, trends, and potential future movements.
- Statistical Methods and Monte Carlo Simulations: Probabilistic and statistical methods borrowed from the kinetic theory of statistical physics are applied to model complex financial systems.
- Monte Carlo simulations allow analysts to simulate random exchanges of wealth between agents, providing a probabilistic understanding of market outcomes and scenarios.
- Applications and Limitations: Kinetic exchange models find applications in understanding income distribution, market bubbles, asset price movements, and extreme events in financial markets.
- These models may oversimplify real-world complexities and should be complemented with other approaches for comprehensive analysis.
The Kinetic Theory of Statistical Physics
The kinetic theory of statistical physics primarily deals with the statistical behavior of a large number of particles.
In this context, particles can be thought of as individual agents or entities in a market.
Just as particles in a gas move and interact based on certain probabilistic rules, agents in a market exchange money or assets based on certain probabilistic rules.
This analogy forms the foundation of kinetic exchange models in financial markets.
Probabilistic and Statistical Methods
The probabilistic and statistical methods used in kinetic exchange models are mostly borrowed from the kinetic theory of statistical physics.
These methods allow for the modeling of complex systems where individual behaviors might be unpredictable, but the collective behavior follows certain patterns or distributions.
In finance, this translates to understanding how individual trading decisions, influenced by a myriad of factors, lead to broader market trends and movements.
Monte Carlo Simulations
The Monte Carlo simulation is one of the most popular tools for those working with kinetic exchange models.
Monte Carlo simulations are computational algorithms that rely on repeated random sampling to obtain numerical results.
In the context of kinetic exchange models, these simulations can be used to model the random exchanges of money or assets between agents.
By running these simulations multiple times, analysts can gain a probabilistic understanding of potential market outcomes and scenarios.
Related:
Applications in Finance
As mentioned, these models are based on the idea that particles (or agents) exchange quantities (like energy in physics or wealth in economics) according to certain rules, leading to emergent statistical distributions.
Here are some potential applications of kinetic exchange models in financial markets:
Wealth Distribution Analysis
One of the primary applications of kinetic exchange models in economics is to understand the distribution of wealth among agents.
By modeling agents who exchange money based on certain rules, one can derive wealth distributions that often resemble real-world observations, such as the Pareto distribution.
Market Dynamics and Price Formation
Kinetic exchange models can be used to understand how prices are formed in markets based on the interactions of various agents.
This can help in understanding the dynamics of stock prices, commodities, bonds, and other financial instruments.
Trading Strategies
By understanding the underlying dynamics of agent interactions, traders might develop strategies that take advantage of certain predictable patterns or behaviors in the market.
Risk Management
Kinetic models can be used to simulate various market conditions and understand the potential risks associated with different scenarios.
This can be particularly useful for portfolio management and hedging strategies.
For example, if risk managers ran a simulation and saw that there’s some chance that a certain portfolio configuration sees a particular drawdown at some frequency that’s not acceptable, they will then look to hedge against this (e.g., options) or look to change the asset allocation.
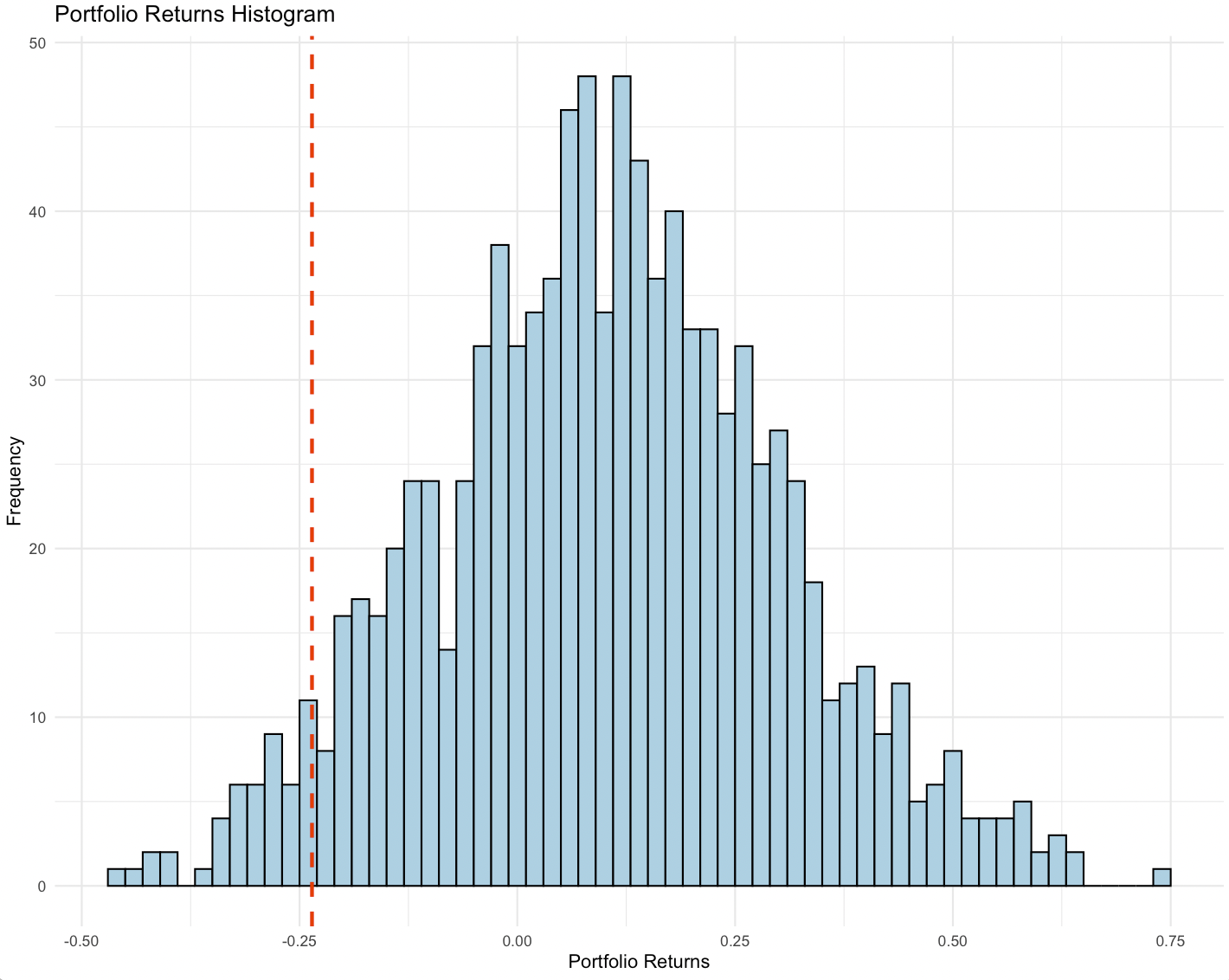
Market Stability and Crashes
By modeling the interactions of agents, one can study the conditions under which a market might become unstable or even crash.
This can provide insights into systemic risks and potential regulatory interventions.
Interbank Lending and Systemic Risk
In the context of banking, kinetic exchange models can be used to understand the dynamics of interbank lending and the potential for cascading failures in the financial system.
Foreign Exchange Markets
Kinetic models can be applied to understand the dynamics of currency exchange rates based on the interactions of various agents in the foreign exchange market.
Behavioral Finance
By incorporating elements of behavioral economics, kinetic exchange models can be used to study how irrational behaviors or biases can impact market dynamics.
High-Frequency Trading
In modern financial markets, a significant portion of trading is done algorithmically at very high frequencies.
Kinetic exchange models can be adapted to study the impact of high-frequency trading on market stability and dynamics.
Market Microstructure
Understanding the microstructure of markets, including how orders are placed, matched, and executed, can benefit from kinetic exchange models, especially when considering the strategic interactions of different market participants.
Commodity Markets
These models can be applied to understand the dynamics of commodity prices, especially in markets where there are a few dominant players or oligopolies.
Innovation and Growth
In a broader economic context, kinetic exchange models can be used to study how wealth and resources are redistributed in an economy, potentially leading to innovation and growth if policymakers or private sector agents can use that information in important ways.
Regulatory Impact Analysis
By simulating markets with different regulatory rules, one can study the potential impacts of various regulatory interventions on market stability, efficiency, and fairness.
Network Effects
Given that modern financial markets are deeply interconnected, kinetic exchange models can be combined with network theory to study the impact of network effects on market dynamics.
Summary
These are just a few potential applications.
The adaptability of kinetic exchange models means that they can be tailored to study a wide range of phenomena in financial markets, depending on the specific questions of interest.
FAQs – Kinetic Exchange Models of Markets
What are Kinetic Exchange Models in the context of markets?
Kinetic Exchange Models are mathematical models used most commonly to describe the dynamics of wealth distribution in markets.
They are inspired by the kinetic theory of gases in physics, where particles exchange energy during collisions.
Similarly, in these models, agents (or economic entities) exchange wealth during transactions.
How are probabilistic and statistical methods applied in Kinetic Exchange Models?
The probabilistic and statistical methods used in Kinetic Exchange Models are primarily derived from the kinetic theory of statistical physics.
This theory provides a robust framework for understanding the random motion of particles and their interactions.
In the context of markets, these methods help in understanding the random nature of transactions and the subsequent distribution of wealth among agents.
Why are Monte Carlo simulations used in solving these models?
Monte Carlo simulations are a class of computational algorithms that rely on repeated random sampling to obtain numerical results.
Given the probabilistic nature of Kinetic Exchange Models, Monte Carlo simulations come in handy in solving these models.
They allow for the modeling of complex systems and the estimation of the distribution of outcomes based on random variables.
How do Kinetic Exchange Models contribute to our understanding of financial markets?
Kinetic Exchange Models provide insights into the inherent inequalities in wealth distribution in financial markets.
By studying these models, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the mechanisms behind wealth accumulation, the emergence of a middle class, and the factors that lead to wealth concentration among a few agents.
These models can be used to understand income distribution within an economy, the formation of market bubbles, and even the dynamics of stock price movements.
They also offer a framework to study and potentially predict extreme market events, such as crashes or sudden spikes.
Are there any limitations to using Kinetic Exchange Models in finance?
While Kinetic Exchange Models offer insights into wealth distribution, they are, after all, simplifications of the real world.
Real-world markets are influenced by a variety of factors, including government policies, technological advancements, and global events, which may not be accounted for in the models.
Therefore, while they provide a foundational understanding, they should be used in conjunction with other models and theories for a more thorough analysis.
How do Kinetic Exchange Models compare to other financial models?
Kinetic Exchange Models focus primarily on the exchange of wealth and the resulting distribution.
In contrast, other financial models might focus on asset pricing and valuation, market behavior, or risk assessment.
While Kinetic Exchange Models provide insights into wealth distribution, they might not be as effective in predicting stock prices or assessing the risk of financial instruments.
Can Kinetic Exchange Models be applied to other fields outside of finance?
Yes, the foundational principles are derived from the kinetic theory of gases and can be applied to any system where entities exchange a conserved quantity.
This includes fields like sociology, where researchers might be interested in studying the distribution of resources or opportunities among individuals.
How have Kinetic Exchange Models evolved over time?
Originally inspired by the kinetic theory of gases in physics, Kinetic Exchange Models have incorporated more complex factors over time, such as taxation, inheritance, and savings.
As researchers continue to study real-world markets and their nuances, the models are refined and expanded to capture these nuances.
Conclusion
The marriage of statistical physics and finance through kinetic exchange models offers a fresh perspective on modeling financial markets and financial/economic phenomena.
By understanding the probabilistic nature of market interactions and leveraging computational tools, analysts and researchers can better understand economies and markets.