Future-Start Options



Future-start options are a sophisticated class of derivative instruments that are a mix of temporal flexibility and strategic optionality in modern financial markets.
These instruments are useful to traders across multiple time horizons while maintaining exposure to future volatility dynamics.
Key Takeaways – Future-Start Options
- Temporal Flexibility – Future-start options decouple strike selection from purchase. They activate at a future date with payment made upfront, which allows for better strategic timing of exposure.
- Valuation Complexity – Their pricing depends on forward volatility, volatility term structure, and volatility pricing models like Heston or SABR, increasing calibration difficulty.
- Institutional Use Cases – Corporations and asset managers use them to hedge future exposures, align with budget cycles, M&A deals, future liabilities (e.g., pension funds), and structure equity overlays post-rebalancing.
- Volatility Arbitrage Opportunities – Traders exploit inefficiencies in forward skew, calendar spreads, and implied vs. realized volatility for relative value trades.
- Unique Risk and Greeks Profile – Greek sensitivities evolve through time. This requires careful dynamic hedging, especially around vega, delta, and correlation shifts.
Structural Architecture and Market Mechanics
Temporal Decoupling Framework
Future-start options fundamentally decouple the option acquisition decision from the strike price determination.
This creates a unique temporal structure that serves specific strategic needs:
Deferred Strike Determination
The strike price is established at a predetermined future date. It’s typically set at or near the spot price at that moment.
Extended Maturity Architecture
The option’s life begins at the forward-start date, extending the total strategic horizon beyond conventional options.
Premium Front-Loading
Payment occurs at inception despite the delayed activation, which creates distinct funding dynamics.
Implied Forward Option Layering
Forward-starts enable the construction of layered optionality across multiple future dates, allowing institutions to structure path-dependent or multi-stage payoff frameworks.
Modular Optionality Design
Forward-starts can be embedded within exotic or structured products.
They offer modular design flexibility where the forward-start leg acts as a building block in hybrid derivatives or autocallables.
Valuation and Model Dependencies
The pricing architecture of future-start options shows critical dependencies on volatility term structure and forward volatility assumptions:
Forward Volatility Extraction
Markets must price the expected volatility from the forward-start date to expiration, not from today.
Term Structure Sensitivity
The shape and dynamics of the volatility term structure become primary valuation drivers.
Correlation Structures
The relationship between spot price movements and volatility evolution gains more importance.
Stochastic Volatility Calibration Challenge
Forward-starts often require dynamic models like Heston or SABR to accurately capture the joint distribution of forward-start price levels and volatility, complicating calibration and increasing model risk.
Strategic Applications in Institutional Portfolios
Corporate Hedging Architectures
Future-start options serve critical functions in corporate risk management frameworks, particularly for entities with predictable future exposures:
Employee Compensation Hedging
Technology companies use these instruments to hedge future stock-based compensation grants.
M&A Contingent Exposures
Corporations hedge potential currency or commodity exposures contingent on deal completion.
Budget Cycle Alignment
Treasury departments align hedging programs with fiscal planning cycles through forward-start structures.
Long-Dated Liability Hedging
Pension funds and insurers use forward-starts to hedge liabilities that begin at a future date.
They give cost certainty today while matching risk onset with projected cash flow schedules.
Benchmark-Tracking Overlay Strategies
Asset managers use forward-start calls to synthetically add equity upside after a benchmark-rebalancing event without triggering pre-event tracking error.
Volatility Arbitrage and Relative Value
Sophisticated traders/investors/market participants exploit structural inefficiencies in forward volatility pricing:
Calendar Spread Enhancement
Future-start options can create synthetic calendar spreads with unique risk-return profiles.
Volatility Surface Arbitrage
Discrepancies between implied and realized forward volatility create systematic opportunities.
Cross-Asset Volatility Trading
Relative value strategies across asset classes using forward-start structures.
Forward Skew Trading
Traders exploit mispricings in the forward skew (the implied volatility smile at the forward-start date) by constructing offsetting trades that isolate forward convexity effects.
Risk Architecture and Greeks Dynamics
Temporal Greeks Evolution
The Greeks behavior of future-start options reveals unique risk management challenges that distinguish these instruments from conventional derivatives:
Vega Dynamics
Future-start options show heightened sensitivity to volatility term structure changes, with vega exposure concentrated on forward volatility rather than spot volatility.
Theta Decay Patterns
The time decay exhibits a dual-phase structure: minimal decay before the forward-start date, followed by accelerated decay post-activation.
Delta Evolution
Delta remains relatively stable pre-activation, then converges toward standard option delta behavior post-strike determination.
Correlation Risk and Model Dependencies
Future-start options embed complex correlation assumptions that create subtle but significant risk exposures:
Spot-Volatility Correlation
The relationship between underlying price movements and implied volatility changes becomes a primary risk factor.
Even small shifts in this correlation can distort forward-start pricing, particularly when embedded in multi-leg volatility structures.
Term Structure Dynamics
Changes in volatility term structure shape create profit and loss variations independent of spot price movements.
Sudden steepening or flattening in the curve can materially impact valuation, even if the underlying remains range-bound.
Model Risk Concentration
Valuation heavily depends on assumptions about forward volatility dynamics, creating model-specific risk concentrations.
Market Microstructure and Liquidity Considerations
Institutional Market Making Dynamics
The market-making ecosystem for future-start options reveals structural complexities that affect pricing efficiency and liquidity provision:
Inventory Management Challenges
Dealers face extended holding periods with uncertain hedging requirements, leading to wider bid-ask spreads.
Dynamic Hedging Complexity
The changing Greeks profile requires dynamic hedging strategies that evolve through the option’s lifecycle.
Capital Allocation Constraints
Regulatory capital requirements for forward-start positions create additional friction in market-making activities.
Price Discovery Mechanisms
Future-start options serve as unique vehicles for price discovery in forward volatility markets:
Forward Volatility Extraction
Market prices reveal consensus expectations about future volatility regimes.
These extracted forward volatilities are critical for structuring long-dated derivatives and forecasting term structure behavior.
Cross-Sectional Information
Comparing forward-start prices across strikes and maturities provides insights into risk premium dynamics.
Volatility Surface Evolution
These instruments help complete the volatility surface in regions where standard options provide limited information.
Anticipated Event Pricing
Future-start options capture market expectations around scheduled macro or corporate events whose impact lies beyond the current option horizon.
Traders use them to isolate volatility linked to earnings, elections, or policy decisions, separated from near-term noise.
Payoff Diagram
A future-start option has a similar-looking payoff diagram to standard options.
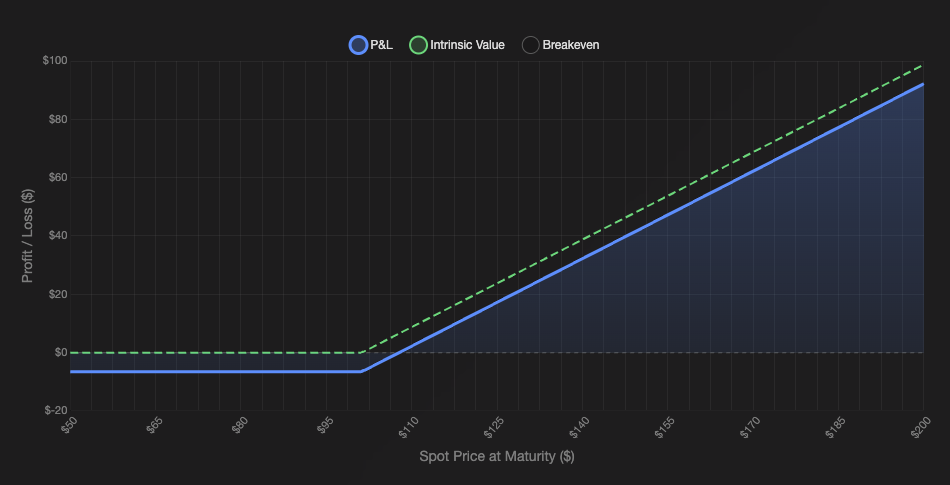
Of course, the payoff diagram will vary depending on the the exact configuration and customization of the instrument.
Related Structured Variants
- Cliquet Options – A series of forward-start options embedded in one instrument (often used in structured products).
- Ratchet Options – Strike price resets periodically, similar to forward-start behavior in discrete intervals.
- Step-Up Options – May mimic forward-start logic through predefined activation triggers.
- Lookforward Options – Less common but conceptually similar; strike price is set based on a future observation.
How Can Individual Traders Gain Access?
Retail traders rarely access pure future-start options directly, as these are typically traded over-the-counter (OTC) or embedded in institutional structured products.
Nonetheless, individuals can gain indirect exposure through structured notes, cliquet options, or products offered by private banks and brokers with derivative desks.
Some brokers provide synthetic strategies using combinations of vanilla options to approximate forward-start behavior.
Additionally, retail traders can analyze implied forward volatility using calendar spreads and design custom strategies around future volatility expectations.
Access requires advanced platforms, margin approval for complex options, and often a high level of trading experience or accreditation depending on jurisdiction.