Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSCA) Brokers 2026



Based in South Africa? Use a broker regulated by the Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSCA) for safety.
After stepping up its oversight of brokers in recent years with tougher penalties for non-compliance resulting in stronger trader protections, FSCA has earned ‘yellow tier’ status in DayTrading.com’s Regulation & Trust Rating.
Check out our pick of the top FSCA-regulated platforms to find the perfect provider for your trading needs.
Best FSCA Brokers
Based on our latest hand-on tests in February 2026, these are the 6 best FSCA-regulated trading platforms:
Here is a summary of why we recommend these brokers in February 2026:
- Exness - Established in 2008, Exness has maintained its position as a highly respected broker, standing out with its industry-leading range of 40+ account currencies, growing selection of CFD instruments, and intuitive web platform complete with useful extras like currency convertors and trading calculators.
- XM - XM is a globally recognized forex and CFD broker with 15+ million clients in 190+ countries. Since 2009, this trusted broker has been delivering low trading fees across its growing roster of 1000+ instruments. It’s also highly regulated, including by ASIC, CySEC and DFSA and SCA in the UAE, and offers a comprehensive MetaTrader experience.
- AvaTrade - Established in 2006, AvaTrade is a leading forex and CFD broker trusted by over 400,000 traders. Operating under regulation in 9 jurisdictions, AvaTrade processes an impressive 2+ million trades each month. Through like MT4, MT5, and its proprietary WebTrader, the broker provides a growing selection of 1,250+ instruments. Whether it’s CFDs, AvaOptions, or the more recent AvaFutures, short-term traders at all levels will find opportunities. With terrific education and 24/5 multilingual customer support, AvaTrade delivers the complete trading experience.
- Trade Nation - Trade Nation is a top FX and CFD broker regulated in multiple jurisdictions including the UK and Australia. The firm offers low-cost fixed and variable spreads on 1000+ assets with robust trading platforms and training materials. The Signal Centre can also be used for trade ideas.
- Vantage - Founded in 2009, Vantage offers trading on 1000+ short-term CFD products to over 900,000 clients. You can trade Forex CFDs from 0.0 pips on the RAW account through TradingView, MT4 or MT5. Vantage is ASIC-regulated and client funds are segregated. Copy traders will also appreciate the range of social trading tools.
- Plus500 - Established in 2008 and headquartered in Israel, Plus500 is a prominent brokerage that boasts over 25 million registered traders in over 50 countries. Specializing in CFD trading, the company offers an intuitive, proprietary platform and mobile app. It maintains competitive spreads and does not charge commissions or deposit or withdrawal fees. Plus500 also continues to shine as one of the most trusted brokers with licenses from reputable regulators, including the FCA, ASIC and CySEC.
FSCA Brokers Comparison
| Broker | FSCA Regulated | ZAR Account | Minimum Deposit | Markets | Platforms | Leverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exness | ✔ | ✔ | Varies based on the payment system | CFDs on Forex, Stocks, Indices, Commodities, Crypto | Exness Trade App, Exness Terminal, MT4, MT5, TradingCentral | 1:Unlimited |
| XM | ✔ | - | $5 | CFDs, Forex, Stocks, Commodities, Indices, Thematic Indices, Precious Metals, Energies | MT4, MT5, TradingCentral | 1:1000 |
| AvaTrade | ✔ | - | $100 | CFDs, Forex, Stocks, Indices, Commodities, ETFs, Bonds, Crypto, Spread Betting, Futures | WebTrader, AvaTradeGO, AvaOptions, AvaFutures, MT4, MT5, AlgoTrader, TradingView, TradingCentral, DupliTrade | 1:30 (Retail) 1:400 (Pro) |
| Trade Nation | ✔ | ✔ | $0 | Forex, CFDs, Indices, Shares, Commodities, Futures, Bonds, Spread Betting, Cryptos (Bahamas Entity Only) | MT4 | 1:500 (entity dependent) |
| Vantage | ✔ | - | $50 | CFDs, Forex, Stocks, Indices, Commodities, ETFs, Bonds | ProTrader, MT4, MT5, TradingView, DupliTrade | 1:500 |
| Plus500 | ✔ | ✔ | $100 | CFDs on Forex, Stocks, Indices, Commodities, ETFs, Options, Crypto | WebTrader, App | ✔ |
Exness
"After slashing its spreads, improving its execution speeds and support trading on over 100 currency pairs with more than 40 account currencies to choose from, Exness is a fantastic option for active forex traders looking to minimize trading costs."
Christian Harris, Reviewer
Exness Quick Facts
| Demo Account | Yes |
|---|---|
| Instruments | CFDs on Forex, Stocks, Indices, Commodities, Crypto |
| Regulator | FCA, FSCA, CMA, FSA, CBCS, BVIFSC, FSC, JSC |
| Platforms | Exness Trade App, Exness Terminal, MT4, MT5, TradingCentral |
| Minimum Deposit | Varies based on the payment system |
| Minimum Trade | 0.01 Lots |
| Leverage | 1:Unlimited |
| Account Currencies | USD, EUR, GBP, CAD, AUD, NZD, INR, JPY, ZAR, MYR, IDR, CHF, HKD, SGD, AED, SAR, HUF, BRL, NGN, THB, VND, UAH, KWD, QAR, KRW, MXN, KES, CNY |
Pros
- Improved execution speeds, now averaging under 25ms, offer optimal conditions for short-term traders.
- Fast and dependable 24/7 multilingual customer support via telephone, email and live chat based on hands-on tests.
- Excellent range of account types for all experience levels, including Cent, Pro plus the introduction of Raw Spread, ideal for day traders.
Cons
- Exness has expanded its range of CFDs and added a copy trading feature, but there are still no real assets such as ETFs, cryptocurrencies or bonds
- Retail trading services are unavailable in certain jurisdictions, such as the US, UK and EU, limiting accessibility compared to top-tier brokers like Interactive Brokers.
- MetaTrader 4 and 5 are supported, but TradingView and cTrader still aren’t despite rising demand from active traders and integration at alternatives like Pepperstone.
XM
"With a low $5 minimum deposit, advanced charting platforms in MT4 and MT5, expanding range of markets, and a Zero account offering spreads from 0.0, XM provides all the essentials for active traders, even earning our ‘Best MT4/MT5 Broker’ award in recent years."
Christian Harris, Reviewer
XM Quick Facts
| Demo Account | Yes |
|---|---|
| Instruments | CFDs, Forex, Stocks, Commodities, Indices, Thematic Indices, Precious Metals, Energies |
| Regulator | CySEC, DFSA, SCA, FSCA, FSA, FSC Belize, FSC Mauritius |
| Platforms | MT4, MT5, TradingCentral |
| Minimum Deposit | $5 |
| Minimum Trade | 0.01 Lots |
| Leverage | 1:1000 |
| Account Currencies | USD, EUR, GBP, JPY |
Pros
- XM has rolled out platform upgrades with integrated TradingView charts and an XM AI assistant, delivering faster execution, smarter analysis, and a sleeker, more intuitive trading experience.
- XM’s Zero account is ideal for day trading with spreads from 0.0 pips, 99.35% of orders executed in <1 second, and no requotes or rejections.
- XM secured a category 5 license from the Securities and Commodities Authority (SCA) of the United Arab Emirates in late 2025, strengthening its regulatory credentials and making it a strong option for traders in the Middle East.
Cons
- XM relies solely on the MetaTrader platforms for desktop trading, so there’s no in-house downloadable or web-accessible solution for a more beginner-friendly user experience with unique features.
- While the XM app stands out for its usability and exclusive copy trading products, the selection of technical analysis tools needs to be improved to meet the needs of advanced traders.
- XM is falling behind the curve by not offering cTrader and TradingView which are increasingly being favored over MetaTrader for their smoother user experience and superior charting packages.
AvaTrade
"AvaTrade offers active traders everything they need: an intuitive WebTrader, powerful AvaProtect risk management, a smooth 5-minute sign-up process, and dependable support you can rely on in fast-moving markets."
Jemma Grist, Reviewer
AvaTrade Quick Facts
| Demo Account | Yes |
|---|---|
| Instruments | CFDs, Forex, Stocks, Indices, Commodities, ETFs, Bonds, Crypto, Spread Betting, Futures |
| Regulator | ASIC, CySEC, FSCA, ISA, CBI, JFSA, FSRA, BVI, ADGM, CIRO, AFM |
| Platforms | WebTrader, AvaTradeGO, AvaOptions, AvaFutures, MT4, MT5, AlgoTrader, TradingView, TradingCentral, DupliTrade |
| Minimum Deposit | $100 |
| Minimum Trade | 0.01 Lots |
| Leverage | 1:30 (Retail) 1:400 (Pro) |
| Account Currencies | USD, EUR, GBP, CAD, AUD |
Pros
- AvaTrade launched AvaFutures to offer low-margin access to global markets, then expanded in 2025 as one of the first brokers to add CME’s Micro Grain Futures, and then later in the year went further by integrating with TradingView.
- The WebTrader excelled in our hands-on tests, sporting a user-friendly interface for beginners, complete with robust charting tools like 6 chart layouts and 60+ technical indicators.
- Years on, AvaTrade remains one of the few brokers offering a bespoke risk management tool, AvaProtect, that insures losses up to $1M for a fee and is easy to activate on the platform.
Cons
- AvaTrade’s WebTrader has improved, but work is still needed in terms of customizability – frustratingly widgets like market watch and watchlists can’t be hidden, moved, or resized.
- The AvaSocial app is good but not great – the look and feel, plus the navigation between finding strategy providers and account management needs upgrading to rival category leaders like eToro.
- Although the deposit process itself is smooth, AvaTrade still doesn’t facilitate crypto payments, a feature increasingly offered by brokers like TopFX, which caters to crypto-focused traders.
Trade Nation
"Trade Nation is a good choice for newer traders looking for a wide range of financial markets on a user-friendly platform. There is no minimum deposit, free funding options and strong education."
William Berg, Reviewer
Trade Nation Quick Facts
| Demo Account | Yes |
|---|---|
| Instruments | Forex, CFDs, Indices, Shares, Commodities, Futures, Bonds, Spread Betting, Cryptos (Bahamas Entity Only) |
| Regulator | FCA, ASIC, FSCA, SCB, FSA |
| Platforms | MT4 |
| Minimum Deposit | $0 |
| Minimum Trade | 0.1 Lots |
| Leverage | 1:500 (entity dependent) |
| Account Currencies | USD, EUR, GBP, AUD, ZAR, SEK, NOK, DKK |
Pros
- A choice of trading platforms and apps, including MT4, make the brand a good fit for savvy traders
- The trading firm offers tight spreads and a transparent pricing schedule
- There is a low minimum deposit for beginners
Cons
- Fewer legal protections with offshore entity
Vantage
"Vantage remains an excellent option for CFD traders seeking a tightly-regulated broker with access to the reliable MetaTrader platforms. The fast sign-up process and $50 minimum deposit make it very straightforward to start day trading quickly."
Jemma Grist, Reviewer
Vantage Quick Facts
| Demo Account | Yes |
|---|---|
| Instruments | CFDs, Forex, Stocks, Indices, Commodities, ETFs, Bonds |
| Regulator | FCA, ASIC, FSCA, VFSC |
| Platforms | ProTrader, MT4, MT5, TradingView, DupliTrade |
| Minimum Deposit | $50 |
| Minimum Trade | 0.01 Lots |
| Leverage | 1:500 |
| Account Currencies | USD, EUR, GBP, CAD, AUD, NZD, JPY, HKD, SGD, PLN |
Pros
- There’s an excellent suite of day trading software, including the award-winning platforms MT4 and MT5
- It’s quick and easy to open a live account – taking less than 5 minutes
- The low minimum deposit of $50 and zero funding fees make this broker a great choice for new traders
Cons
- Unfortunately, cryptos are only available for Australian clients
- A steep $10,000 deposit is needed for the best trading conditions, which include the $1.50 commission per side
- The average execution speeds of 100ms to 250ms are slower than alternatives based on tests
Plus500
"Plus500 offers a super-clean experience for traders with a CFD trading platform that sports a modern design and dynamic charting. That said, the broker’s research tools are limited, fees trail the cheapest brokers, and there’s room for enhancement in its educational resources."
Christian Harris, Reviewer
Plus500 Quick Facts
| Demo Account | Yes |
|---|---|
| Instruments | CFDs on Forex, Stocks, Indices, Commodities, ETFs, Options, Crypto |
| Regulator | FCA, ASIC, CySEC, DFSA, MAS, FSA, FSCA, FMA, EFSA |
| Platforms | WebTrader, App |
| Minimum Deposit | $100 |
| Minimum Trade | Variable |
| Leverage | Yes |
| Account Currencies | USD, EUR, GBP, AUD, ZAR, CZK |
Pros
- Plus500 provides a specialized WebTrader platform designed explicitly for CFD trading, offering a clean and uncluttered interface
- In 2025 Plus500 added new share CFDs in emerging sectors like quantum computing and AI, offering opportunities in stocks like IonQ, Rigetti, Duolingo, and Carvana.
- Plus500 has recently bolstered its suite of short-term trading products, including introducing VIX options with enhanced volatility and extended hours trading on 7 stock CFDs
Cons
- Educational resources are limited compared to best-in-class brokers like eToro, impacting the learning curve for beginners
- Compared to some competitors, especially IG, Plus500’s research and analysis tools are limited
- The absence of social trading means users can’t follow and replicate the trades of experienced traders
Methodology
To list the best brokers authorized by the FSCA, we:
- Took our evolving directory of 140 trading providers to identify those claiming FSCA authorization.
- Ran their details through the FSCA’s List of Regulated Persons and Entities for verification, which has had a design upgrade.
- Combined the results of our personal tests with 200+ data points to rank the very best FSCA-regulated firms.
How Can I Check If A Broker Is Regulated By The FSCA?
Here’s a step-by-step guide to verifying a broker’s FSCA status, with a practical example using IG, a well-known CFD and forex broker operating in South Africa.
If you’ve traded in our industry, you’ll know of IG. They’re a quoted firm on the UK FTSE and have a solid reputation as a fair, honest, and competitive brokerage that prides itself on compliance and efficacy.
I expect IG to get a clean bill of financial health from any financial authority’s database I search.However, I’m using IG to highlight the diligence you should engage in before depositing your hard-earned funds into any broker’s account, even if they have a solid reputation for integrity.
You should absolutely conduct such diligence if you’re considering trading with a smaller, less-known broker. A search only takes a few minutes of research.
Step 1. Visit The FSCA’s Official Website
Go to the official FSCA website.
The FSCA maintains an online database of licensed Financial Services Providers (FSPs).
Step 2. Access The “Search For An FSP” Section
You’ll discover the page you need after you click the “Regulated Entities” tab and scroll to the “List of Regulated Entities and Persons”, then depending on the type of provider, e.g. “OTC Derivatives Provider”.
This facility allows you to search for registered brokers by name. The look and feel has been revamped but it’s still easy to use.

Step 3. Enter The Broker’s Details
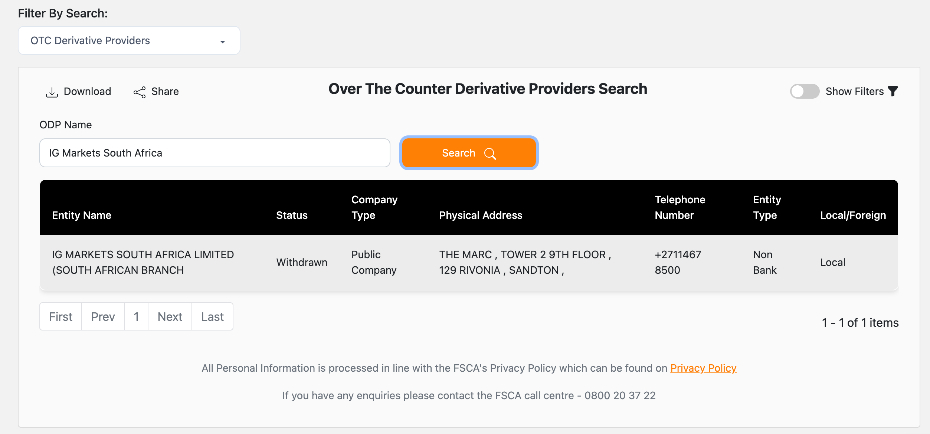
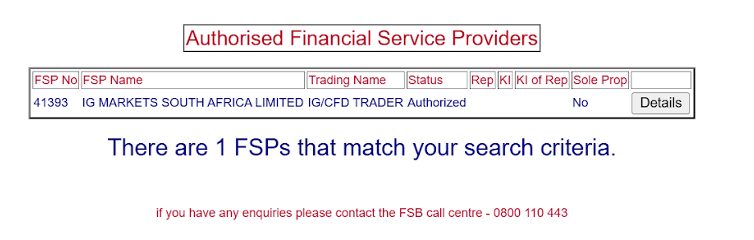
Input the broker’s named entity. This is often found on their website or promotional materials. I typed “IG Markets South Africa“. The IG website also lists its FSCA licence number – FSP No 41393.
Step 4. Review The Search Results
Once you’ve entered the details:
- Confirm that the broker appears in the search results.
- Check the broker’s FSP status to ensure it is active and valid.
- Review the services they are licensed to offer (eg CFDs and forex are common at day trading brokers in South Africa).
For IG, our latest search result confirmed that the licence has been withdrawn. This has changed since we previously ran the check, where it was still listed as authorized – screenshots below for reference.
Step 5. Verify Contact Details
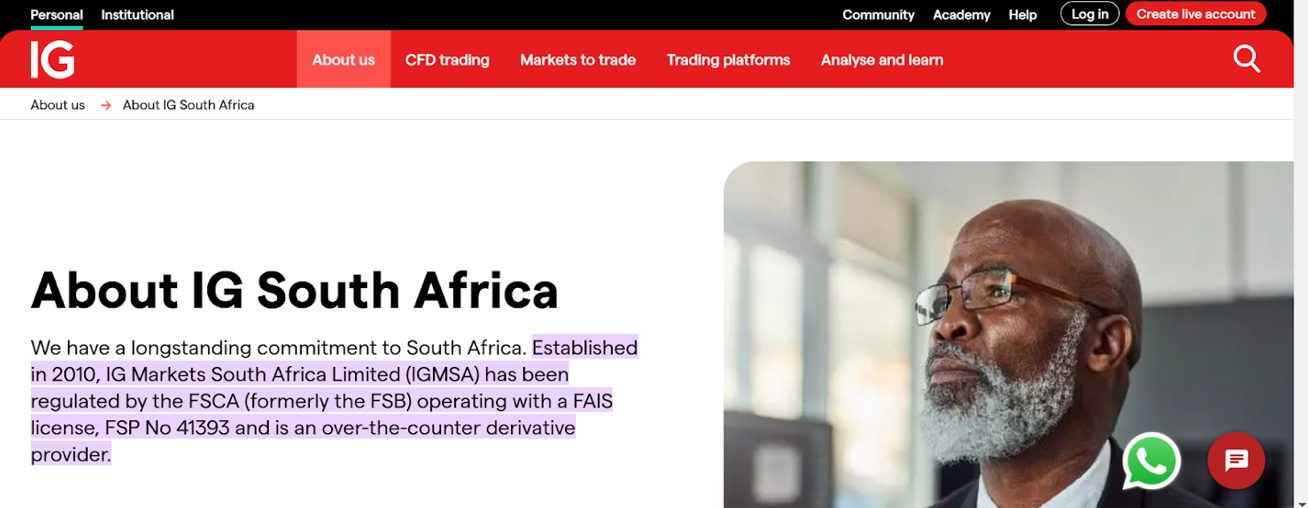
If you’re using a lesser-known trading provider, compare the contact details listed on the FSCA website with those on the company’s official site.
Discrepancies could indicate a fraudulent entity impersonating a regulated brokerage.
Step 6. Look For Public Warnings
The FSCA occasionally issues warnings about unregulated or suspicious brokers. In fact, we’ve seen the volume of these increase in recent years as it’s improved its oversight of online brokers.
Step 7. Contact The FSCA (If Needed)
If you’re unsure about the search results or need further assistance, you can:
- Call: +27 (0)12 428 8000
- Email: info@fsca.co.za
Red Flags To Watch For
- The broker claims to be FSCA-regulated but isn’t listed in the database.
- The broker’s FSP licence is inactive, suspended, or does not cover the services they are offering.
- They avoid sharing their FSP number or providing proof of regulation.
By verifying a broker’s FSCA registration, you can ensure you’re dealing with a legitimate provider and help protect yourself from potential fraud or scams targeting South African traders.
What Is The FSCA?
The Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSCA) exists to oversee and regulate South Africa’s financial services sector to ensure it operates fairly, transparently, and in the best interest of consumers like us active traders.
Before the Financial Sector Conduct Authority was formed in 2018, South Africa’s primary regulator was the Financial Services Board (FSB).
Unfortunately, the FSB was unable to prevent a number of scandals, especially in the pension funds industry. These issues led to investigations and the subsequent signing of the FSR Act, which among several changes, dissolved the FSB and led to the creation of the FSCA.
The FSCA’s core focus is on market conduct – how financial institutions and service providers interact with their customers and the integrity of the financial markets overall.
Key Objectives:
- Protect Consumers: The FSCA ensures that financial services providers treat customers like day traders fairly, provide transparent information, and adhere to ethical practices.
- Promote Market Integrity: It works to maintain trust and confidence in South Africa’s financial markets by enforcing compliance with laws and addressing misconduct.
- Ensure Financial Stability: By regulating the conduct of financial institutions, the FSCA helps maintain stability in the financial system, reducing the risk of systemic crises caused by misconduct or mismanagement.
- Educate And Empower Consumers: The FSCA actively promotes financial literacy to help consumers, such as the growing class of online traders in South Africa, make informed decisions, understand their rights, and recognize potential risks.
- Monitor And Regulate Service Providers: The FSCA oversees entities such as banks, insurance companies, retirement funds, trading firms, and financial advisors, ensuring they meet required standards.
In short, the FSCA exists to foster a healthy financial ecosystem where businesses can thrive, consumers and traders like us are protected, and trust in the system remains strong.
Who Does The FSCA Answer To?
The FSCA is answerable to the South African government, specifically through its alignment with the National Treasury.
It operates under the oversight of the Minister of Finance, who is responsible for ensuring that the FSCA fulfils its mandate following national financial legislation and policy objectives.
Governance Structure:
- The FSCA Commissioner And Deputy Commissioners: The FSCA is led by a Commissioner and a team of Deputy Commissioners, who oversee its operations and ensure compliance with its regulatory duties.
- The Financial Stability Oversight Committee (FSOC): The FSCA collaborates with this committee, which includes representatives from the South African Reserve Bank (SARB) and other regulators, to ensure systemic stability across the financial sector.
- Parliamentary Accountability: The FSCA is ultimately accountable to South Africa’s Parliament. It must submit annual reports and provide updates on its performance and activities to relevant parliamentary committees.
What Powers Does The FSCA Have?
The Financial Sector Conduct Authority has extensive powers to regulate and oversee South Africa’s financial markets and online trading providers.
Key Powers:
- Regulatory And Supervisory Authority – The FSCA regulates a wide range of financial institutions, including investment firms. It sets and enforces rules on market conduct, ensuring compliance with South Africa’s financial laws and standards.
- Licensing And Registration – The FSCA has the power to issue, renew, suspend, or revoke licences for financial services providers (FSPs), including brokers. It ensures that only qualified and compliant entities operate within the financial sector.
- Investigation And Enforcement – The FSCA can investigate misconduct, fraud, or breaches of financial laws and regulations. It has the authority to impose penalties, fines, or administrative sanctions on entities and individuals who violate the rules and can initiate legal proceedings against offenders when necessary.
- Market Surveillance And Oversight – The FSCA monitors market activity to identify and address unfair practices, insider trading, or market manipulation. It oversees the conduct of trading platforms and other financial infrastructure.
- Consumer Protection And Education – The FSCA develops and enforces policies to ensure that consumers are treated fairly by financial service providers. It conducts awareness campaigns and financial literacy programs.
- Rule-Making Authority – The FSCA can issue directives, guidelines, and regulations to clarify financial legislation and promote best practices across the sector.
- Collaboration With Other Regulators – It works with bodies like the South African Reserve Bank (SARB) and Prudential Authority to ensure financial stability and address cross-sector issues.
Enforcement tools:
The FSCA can take decisive actions, such as:
- Freezing bank accounts or assets linked to misconduct
- Issuing public warnings about unregistered or fraudulent trading providers
- Suspending trading activities in cases of severe breaches
What Rules Must An FSCA Broker Follow?
Brokers regulated by the Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSCA) must adhere to a comprehensive set of rules designed to ensure transparency, fairness, and consumer protection.
These rules cover how brokers operate, interact with clients like you and me, and manage risk.
Key rules:
- Licensing And Registration – Before offering services, brokers must obtain a valid Financial Services Provider (FSP) licence. They must display their FSP licence number prominently on their website, communications, and marketing materials.
- Suitability Assessments – Brokers are required to assess whether their financial products and services are suitable for their clients’ needs, experience, and risk tolerance. This is especially important as a day trader, where the risk of incurring losses is high.
- Risk Disclosure – Brokers must disclose all risks associated with financial instruments, such as CFDs or forex trading, to ensure clients fully understand potential losses. Notably for short-term traders, brokers must inform retail investors about potential losses due to leverage trading.
- Segregation Of Client Funds – Client funds must be held in segregated accounts, separate from the broker’s operational funds. This protects your money in case the brokerage faces financial difficulties.
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Compliance – Brokers must implement strict Anti Money Laundering (AML) policies, including verifying the identity of clients (Know Your Customer/KYC checks) and reporting suspicious transactions to authorities.
- Transparent Pricing And Fees – All fees, commissions, spreads, and other charges must be disclosed clearly to clients. Traders are protected from undisclosed charges or deceptive pricing practices.
- Advertising And Marketing Standards – Marketing materials must be accurate, not misleading, and comply with FSCA guidelines. Claims of guaranteed profits or minimized risks are strictly prohibited.
- Regular Reporting And Audits – Brokers must submit regular compliance reports to the FSCA. They are subject to periodic audits to ensure adherence to regulatory requirements.
- Complaint Handling – Brokers must have an accessible and effective complaints resolution process to address client grievances. They must inform clients of their right to escalate unresolved complaints to the Ombud for Financial Services Providers (FAIS Ombud).
- Risk Management Practices – Brokers must maintain sufficient capital reserves to meet their financial obligations and safeguard clients’ funds. They must implement risk management systems to protect the business and their clients.
- Anti-Market Manipulation Oversight: Brokers must not artificially influence asset prices to disadvantage traders. They also oversee conflicts of interest, ensuring brokers do not trade against their clients unfairly.
- Capital and Operational Requirements – Brokerages must maintain adequate capital reserves to cover their financial obligations and protect traders. This reduces the risk of broker default, ensuring the safety of traders’ funds.
- Continuous Supervision and Updates – The FSCA monitors global trends and updates its regulations to protect active traders in South Africa in a fast-evolving market.
By regulating brokers, enforcing transparency, and monitoring market conduct, the FSCA provides us traders with a safer trading environment, reducing risks and empowering us to trade confidently.
Does The FSCA Have Teeth?
While it may not have the direct enforcement powers of a law enforcement agency, the FSCA is equipped with significant authority to maintain order, impose penalties, and take legal action against entities that break the rules.
And although it’s relatively young with limited enforcement actions under its belt compared to many leading regulators in our industry (the SEC in the US dates back to 1934), the FSCA’s “teeth” are increasingly coming into play.
Here are some notable examples:
- Kabelo Emanuel Mogale (2024): The FSCA imposed a significant penalty of R1,015,315.87 on Mogale, a forex trading signals provider, and debarred him for 10 years. This action was taken because Mogale provided forex trading signals via Telegram without a financial services provider license, which the FSCA considers a financial service requiring proper authorization.
- JP Markets SA (Pty) Ltd (2023): The FSCA fined this forex broker R100,000 for contravening regulations governing over-the-counter (OTC) derivatives trading. JP Markets enabled clients to trade CFDs on forex pairs, shares, and indices without being suitably authorized.
Bottom Line
Verifying that the FSCA regulates a CFD or forex broker is crucial for South African traders to ensure they are dealing with a legitimate and compliant financial services provider.
By utilizing the FSCA’s FSP search function, you can confirm whether a broker, such as IG Markets South Africa, is authorized to operate and provide specific financial services.
For us traders, staying informed about a broker’s regulatory status is not just about compliance – it’s about safeguarding your investments.
To get started, see our pick of the best FSCA-regulated brokers for day traders.





