Synthetic Put

A Synthetic Put is a trading strategy that allows an investor to mimic the payoff of a put option using a combination of stock and options.
How to Create a Synthetic Put
Specifically, a Synthetic Put involves:
- Short selling a stock, and simultaneously
- Buying a call option on that same stock with an in-the-money (ITM) strike price
By combining these two positions, the investor creates a synthetic position that behaves like a put option.
If the stock price falls below the strike price of the call option, the option will be out-of-the-money, and the stock will be the driving force for the profitability of the trade.
Conversely, if the stock price rises, the option will gain value, but the investor will still be short the stock. The trade will lose value in this case due to the premium paid for the option.
When Is the Synthetic Put Useful?
A Synthetic Put can be useful for traders/investors who want to protect their downside risk in a stock they already own or to make a bet on the market falling (when used as a standalone trade).
By creating a Synthetic Put on a stock they already own, traders/investors can limit their potential losses if the stock price falls while still allowing for potential gains if the stock price rises.
Additionally, Synthetic Puts can be a more cost-effective alternative to doing some other types of trades, as they generally require a lower capital requirement.
Short selling also provides a cash credit, which can help generate carry (when the cash is invested with interest and in excess of the borrowing costs of shorting the stock) or offset borrowing costs elsewhere.
Risks and Limitations of the Synthetic Put
There are risks and limitations to using a Synthetic Put.
For example, if the stock price remains relatively stable, the option will expire worthless and the investor will be left with a loss.
The trader will also face any borrowing costs associated with shorting the stock.
As with any investment strategy, it’s important to carefully consider the risks and potential benefits before implementing a Synthetic Put.
Synthetic Put Payoff Diagram
The payoff diagram generally appears as having a fixed downside while generally having a large upside.
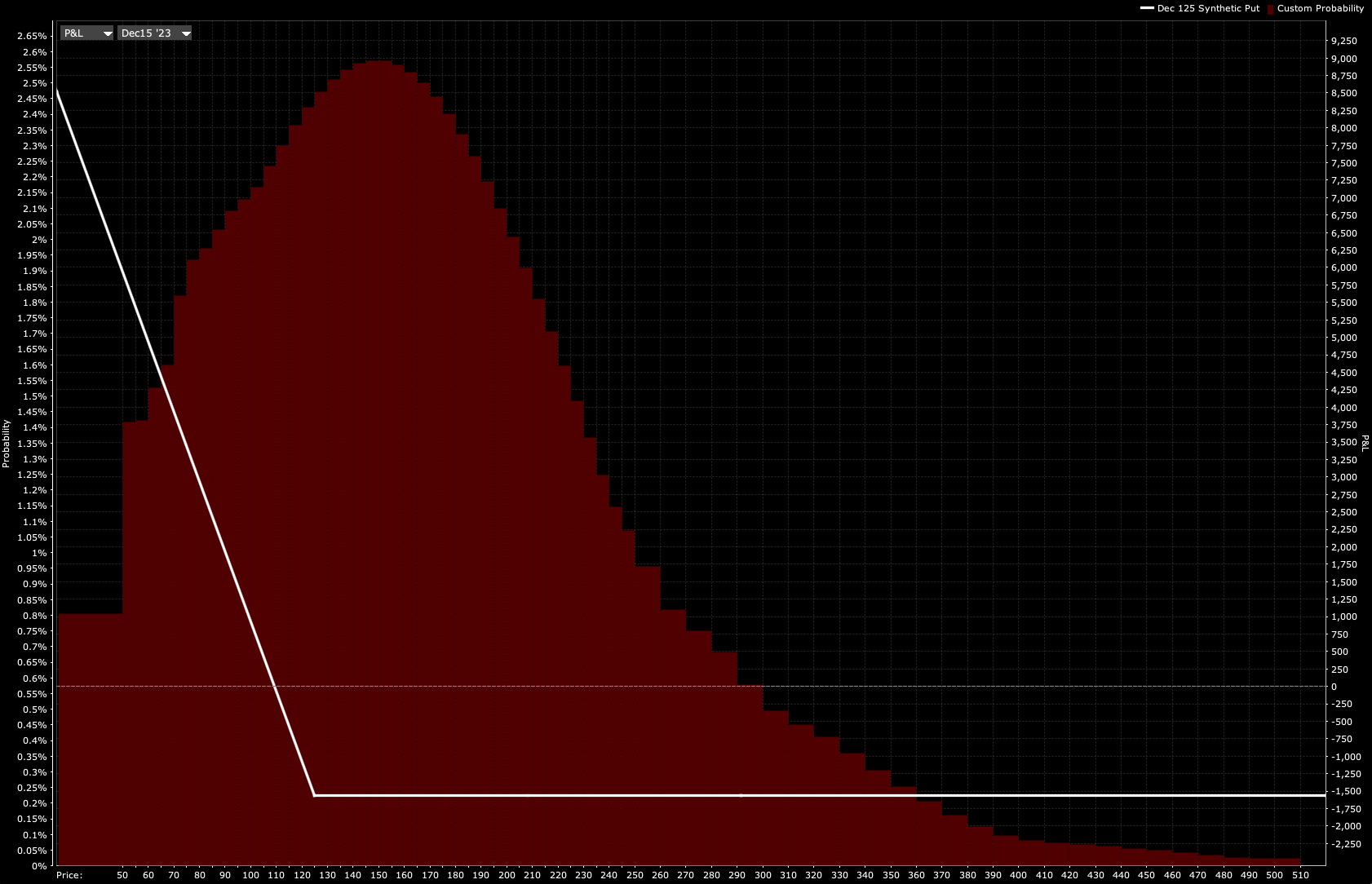
The extent of the possible downside and possible upside is largely dependent on the inherent moneyness of the Synthetic Put.
A Synthetic Put that’s deeper OTM will have less downside and higher upside than one that’s closer to ITM to reflect the underlying probability of the Synthetic Put paying out.