Spot Trading



Spot trading is done in a type of market in which goods or services are traded immediately for cash. Buyers and sellers will make a deal, and the transaction is done “on the spot” – i.e., completed straightaway.
The relative simplicity of spot trading compared with derivatives like futures or options makes it popular. Spot trading also suits short-term traders because of low costs and access to diverse, highly liquid markets.
Quick Introduction
- Spot trading refers to the buying or selling of a security for settlement either immediately or within two business days, known as T+2.
- The majority of spot trading is conducted over the counter (OTC) rather than on regulated exchanges. OTC markets can be done between any two consenting parties.
- Forex, cryptocurrencies and commodities are all popularly traded with the use of spot contracts, providing diverse day trading opportunities.
Best Spot Trading Brokers
Following our in-depth tests, these are the 4 highest rated brokers for spot trading:
How Did We Choose The Best Brokers For Spot Trading?
- We confirmed the broker permits spot trading on its platform.
- We prioritized brokers with low spot trading fees and non-trading fees like deposit/withdrawal charges.
- We chose spot trading brokers with excellent and responsive customer support based on our hands-on tests.
- We favored brokers with well-designed trading platforms with a user-friendly interface and features to help you discover spot trading opportunities.
- We selected online brokers with strong educational tools to help new traders understand how the spot market works.

What Is Spot Trading?
With spot transactions, the exchange of the asset and payment occurs either immediately or shortly after the trade is executed.
On-the-spot trades typically complete within two business days (often expressed as T+2).
Spot prices are influenced by the classic forces of supply and demand, and the terms of these transactions are generally quite simple compared with those of most other financial instruments.
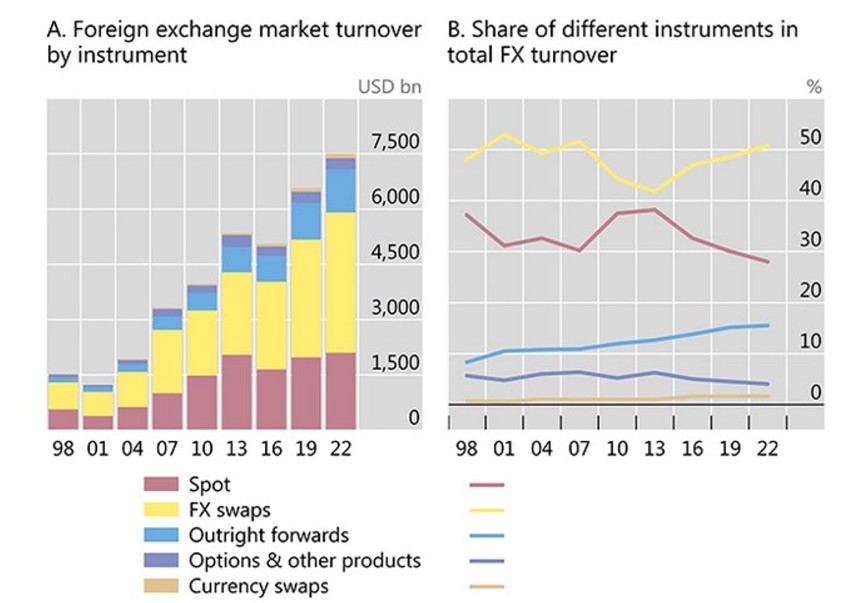
The foreign exchange (or forex) market is among the most popular venue for spot traders, with daily trading volumes reaching over $2 trillion in recent years.
According to the Bank for International Settlements, the daily value of spot transactions in the currency market is steadily growing. However, the proportion of these trades continued to decline relative to derivatives.
Where Does Spot Trading Take Place?
There are two ways that spot traders go about their business:
- Most transactions are carried out over the counter (OTC), where buying and selling take place directly between two parties.
- But contracts (particularly those involving cryptocurrencies) also change hands on centralized financial exchanges.
Trading over the counter (or off-exchange) has certain advantages for investors. These include client privacy, lower trader costs, better contract customization and the opportunity for market participants to deal 24/7.
However, OTC trading exposes you to a greater risk of fraud and market manipulation due to a lack of regulatory oversight.
A lack of transparency on key information, such as pricing and volumes, is another major drawback, as is the threat of counterparty risk (where one party fails to meet its financial obligations).
How Spot Trading Works
Trading on the spot is intuitive, easy to grasp, and lends itself to multiple trading strategies. This all means it is a popular first step for those who are new to short-term trading.
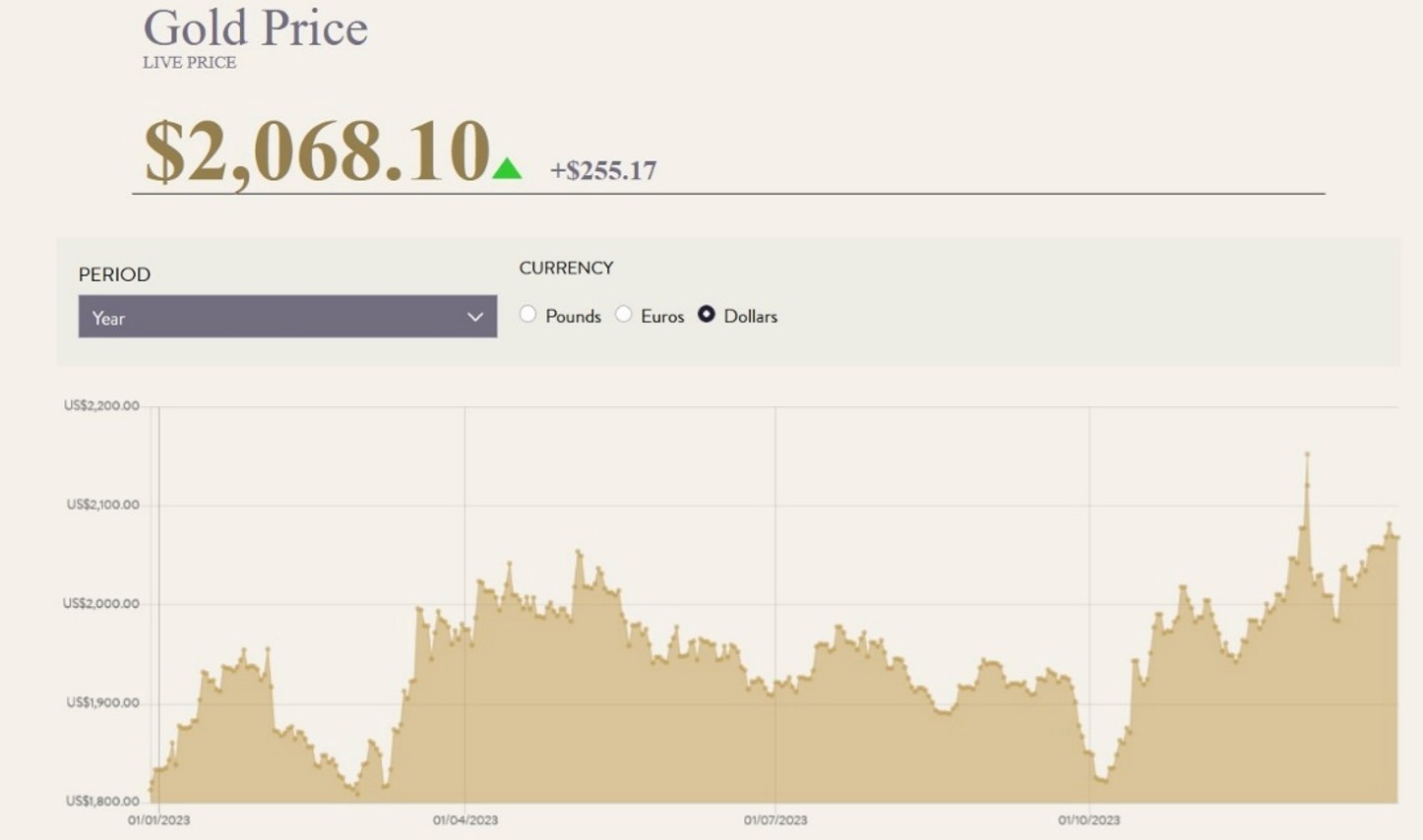
Let’s say that I wish to purchase spot gold in US dollars…
Today, the yellow metal is changing hands at $2,068.10 per ounce, as you can see below.
I expect prices to appreciate from current levels, a scenario which would allow me to make a profit by selling higher at a later date.
The first step on my trading journey is to find a broker who will allow me to buy the commodity in my desired currency (this shouldn’t be a difficult task given the popularity of precious metals trading in dollars!).
Once I’ve selected a brokerage, I’ll place a spot buy order at my desired price and quantity.
If I find a seller who is happy to accept my offer, the deal will be executed, and the gold will be transferred to my portfolio.
The transaction should be settled within two business days of completion.
Spot Trading vs Futures Trading
When someone references the spot market, it means the current price that can be transacted in for the current month’s (or period’s) delivery.
For instance, when people say something like “oil is $100 per barrel” they are often referencing the spot market. The price in other months, up to many years down the road, is often called term pricing.
The shape of the entire curve is often called the futures term structure.
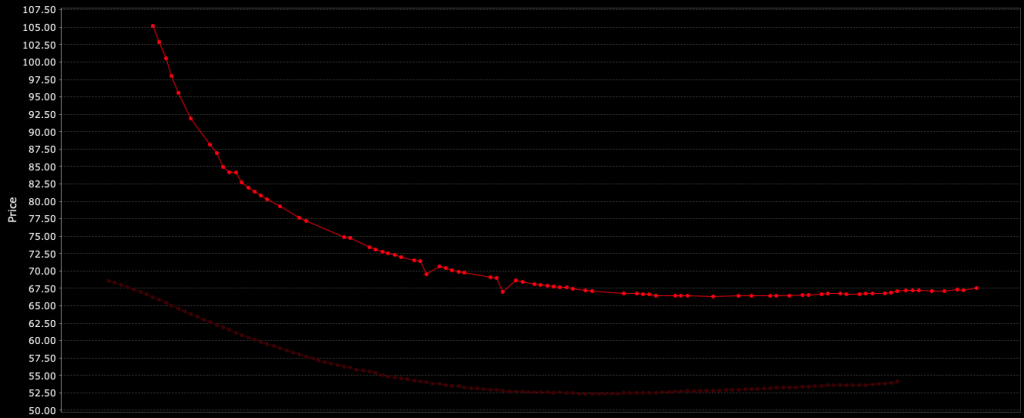
The following chart is an example of the price curve of WTI crude oil. It shows a relatively high spot price, but with futures prices up to $40 lower in future years.
The shape of the curve is called backwardation, where the spot price is above prices in the future.
Futures are also derivatives. This means that – like forwards and options contracts – they get their price from the value of an underlying security such as a commodity or a currency pairing.
Importantly, traders in these complex financial instruments do not actually own the underlying asset.
In the case of a GBP/USD futures contract, for example, I can speculate on the movement of the British pound to the US dollar without having to own any actual currency.
Traders in these derivatives can choose to liquidate their position before the expiration date to avert having to take delivery.
You also have the option of rolling over your position, which involves exiting an expiring contract and entering a new one with a later expiration date.
Furthermore, futures trading involves agreeing to buy or sell a set amount of a financial security at a specified price and by/on a pre-selected date.
Both exchange and settlement take place some time in the future, unlike spot contracts where settlement takes place on the spot or within 48 business hours.
So, which is better?
Spot trading is much simpler than dealing in futures contracts, while it also allows more flexibility as market participants are not bound by pre-determined rules on contract timings and sizes.
However, derivative products also have some significant advantages over spot contracts. Going short – which allows you to make money when the price of an asset falls – is much more straightforward with futures contracts. This function also allows you to hedge against potential losses.
It is also much easier for short-term traders to access leverage (or borrowed funds) with derivatives, which can allow you to make greater profits (and losses).
The bulk of futures trading also takes place on financial exchanges, which (as I explained above) can have major benefits for traders.
Pros And Cons Of Spot Trading
Pros
- Simplicity: Unlike many other financial instruments (and especially derivatives products), the immediate and straightforward nature of spot trading makes it much easier for new traders to get started.
- Rapid settlement: Transactions in forex and commodities markets are usually completed within two business days, while cryptocurrency trades settle straight away.
- High liquidity: The spot market is deep with both buyers and sellers, making it easier for day traders to enter and exit positions and reduce the risk of slippage (where the execution price differs from the quoted price).
- Smaller trades: Spot trading offers the possibility to invest smaller amounts, unlike derivative contracts which often have minimum requirements.
- Leverage opportunities: While not as widely used as in derivatives trading, some brokers allow spot traders to use borrowed funds to potentially ramp up profits. Remember, though, that leverage can also magnify losses when markets move in unexpected directions.
Cons
- OTC challenges: Most spot trades take place outside financial exchanges, resulting in problems like a lack of transparency and counterparty risk.
- Delivery issues: Unlike derivatives traders, who hold contracts without actual ownership of the underlying security like a commodity, dealers in spot contracts commit to physically taking possession of an asset. This can introduce challenges related to storage and logistics.
- Immediate settlement: A spot trade involves the immediate exchange of assets, which means you must have the full amount of capital on hand at the time of the trade.
Bottom Line
The spot market is a type of market in which goods or services are traded immediately for cash. It is popularly used for goods and services that are perishable or that have a short shelf life.
Spot trading is an easy concept to understand, which makes it an ideal starting point for traders who are just starting out. The method of asset pricing is extremely simple, while spot transactions are generally simpler in terms of contractual obligations and conditions compared with derivatives.
On the other hand, trading vehicles like futures can allow traders to employ more complex trading strategies, while the availability of leverage is also far better with derivatives.
Ultimately, your decision to deal in spot contracts or derivatives will depend on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and level of trading expertise.
To get started, open an account with one of our top-rated spot trading brokers. They have all been reviewed and vetted by our testing team.
Article Sources
- Guide to Financial Markets: Why They Exist and how They Work
- Financial Times Guide to Investing, The: The Definitive Companion to Investment and the Financial Markets, The FT Guides
- Triennial Surveys - Bank for International Settlements
The writing and editorial team at DayTrading.com use credible sources to support their work. These include government agencies, white papers, research institutes, and engagement with industry professionals. Content is written free from bias and is fact-checked where appropriate. Learn more about why you can trust DayTrading.com



