Bitcoin Perpetual Futures



Bitcoin perpetual futures allow you to trade Bitcoin on leverage without worrying about expiration.
Traditional futures always settle on a set date, but perpetual futures roll on forever.
That flexibility makes them one of the most popular products in crypto trading today.
Given Bitcoin’s natural volatility – generally between 20%-150% annualized (though declining over time) – the risk of Bitcoin futures is that it can multiply both profits and losses in ways that surprise even experienced traders.
Annualized BTC Volatility
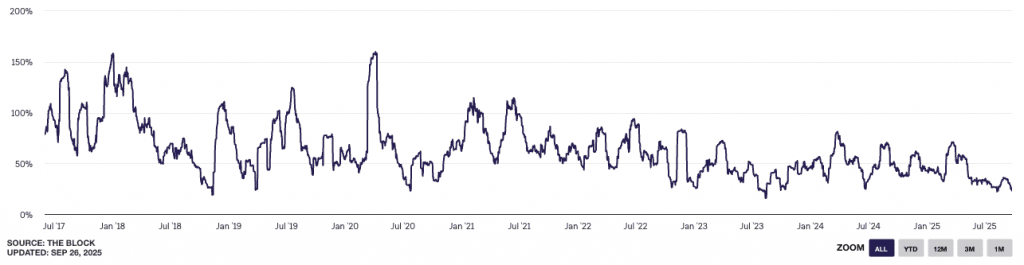
Understanding how they work is the difference between smart use and painful lessons.
We look at what to know below.
Key Takeaways – Bitcoin Perpetual Futures
- Perpetual futures – often called “perps” – let you trade Bitcoin with no expiry, unlike traditional futures.
- Leverage amplifies gains and losses, making risk management non-negotiable.
- The funding rate balances perp prices with spot, creating opportunities to earn or pay small fees.
- Common Strategies/Uses
- Directional bets allow profit from both rising and falling Bitcoin markets.
- Hedging helps long-term holders protect against short-term downside.
- Funding and basis trades give advanced traders ways to capture non-directional returns.
- Major exchanges like Binance, Bybit, OKX, Bitmex, and Kraken offer deep liquidity and flexible leverage.
- Perps can reward discipline but punish carelessness.
- Respect leverage, set stop-losses, and always trade within your means.
What Are Bitcoin Perpetual Futures?
A Simple Definition
Bitcoin perpetual futures – often called “perps” – are contracts that let you bet on Bitcoin’s price without ever owning the coin itself.
Unlike traditional futures that expire on a set date, perpetuals are designed to last forever.
You can hold a position as long as your margin covers it. This makes them feel more like trading Bitcoin directly, but with the added twist of leverage.
Why They Became Popular
Perpetual futures exploded in popularity because they solved a problem in crypto markets: how to trade with leverage 24/7 without the hassle of rolling over contracts. (In stock, bond, and commodity futures, it’s common to roll contracts every 2-3 months.)
Traders loved the flexibility of staying in a position for hours, days, or even months without worrying about expiry.
They also opened the door to a range of strategies.
Speculators use leverage to amplify returns, sometimes turning small price moves into huge gains.
Hedgers, like long-term Bitcoin holders, use perps to protect themselves against sudden price drops by shorting the market.
Others take advantage of the funding rate system to earn yield, essentially getting paid to hold certain positions.
For example, if a trader notices funding is strongly positive, this means longs must pay shorts. If they open a short position in futures and hold it, they collect payments every eight hours, even if Bitcoin’s price barely moves.
Of course, the price can go against them and even swamp the yield, causing a loss.
Let’s summarize the basics:
| Feature | Description |
| No Expiry Date | Can be held forever (hence “perpetual”). |
| Leverage | Allows traders to open positions larger than their capital (e.g., 10x, 25x, even 100x). |
| Funding Rate Mechanism | Keeps the contract price close to the spot price of Bitcoin. |
| Long or Short Positions | Bet on price going up (long) or down (short). |
| Traded on Crypto Exchanges | Available on platforms like Binance, Bybit, OKX, Bitmex, Kraken, etc. |
Key Features
No Expiry Date
Traditional futures come with a ticking clock. At some point, your contract expires and settles.
There’s often no deliverable (if you trade cattle, they won’t drop a bunch of cows off at your house), so you have to “roll” the contracts forward, i.e., into the next expiry.
Perpetual futures broke that mold.
They’re built to mirror spot trading, only with extra firepower. That means you can stay in a position for hours, days, or months. There’s no calendar forcing you out or need to remember when to roll.
The only thing that decides whether you keep your trade open is your margin and your willingness to hold.
Leverage
Leverage is the part that excites people and should also scare them at the same time. With it, you control more Bitcoin than you actually own.
A small $1,000 stake can command $10,000 worth of BTC at 10x leverage. If the price moves in your favor, your gains multiply.
But if the market tilts against you, losses can get bad in a hurry. At high leverage, a minor dip can wipe you out entirely.
Funding Rate: Keeping Prices in Line
Since these contracts never expire, exchanges use a mechanism called the funding rate to keep the perpetual price close to Bitcoin’s real-world spot price.
Every few hours, traders pay or receive small fees depending on which side of the market is more crowded.
It’s not a huge cost in the short term, but over time, it shapes how traders position themselves.
Long or Short
Finally, perpetual futures let you profit whether Bitcoin climbs or crashes. Go long if you believe the price is rising, or short if you think it’s about to fall.
Some use it for other strategies.
For example, if someone has a lot of exposure to equities, they might short Bitcoin believing that a risk-off event is likely to hit “excess liquidity” assets the hardest, helping offset their losses.
That flexibility is what makes perps so compelling. They give traders the freedom to ride the wave in either direction.
How They Work
Opening a Position: Margin and Leverage
Trading a Bitcoin perpetual future starts with collateral, known as margin. You deposit funds – usually BTC, USDT, or USD – into the exchange.
From there, you pick your leverage. Ten times leverage means that for every $1,000 you put down, you control $10,000 worth of Bitcoin.
Once you’ve chosen leverage, you decide your direction: go long if you expect Bitcoin to rise, or go short if you think it will drop.
Naturally, as we just covered above, it may depend on what else a trader owns (e.g., hedging against other parts of a portfolio).
Example
Let’s say Bitcoin trades at $60,000.
You put in $1,000 with 10x leverage, giving you control over about $10,000 of Bitcoin.
If Bitcoin climbs 10%, your position gains $1,000. That’s a 100 percent return on your margin.
The positive aspect is obvious: small moves in Bitcoin translate into outsized profits. But the knife cuts both ways.
If Bitcoin falls 10% instead, your $1,000 margin is gone. You’ll need to post more right away or face liquidation, or the automatic closing of your trade when losses consume your deposit.
The Funding Rate: Balancing the System
Since perpetual contracts don’t expire, they need a mechanism to stay anchored to the spot market…
Enter the funding rate.
Every eight hours, longs and shorts exchange a small payment.
If the perpetual contract is trading higher than spot, longs pay shorts.
If it trades lower, shorts pay longs. Think of it as a fee or rebate that nudges traders back toward balance.
Mark Price vs. Last Price
Exchanges also use a special safeguard called the mark price. Instead of calculating profits and losses solely from the last traded price, which can be manipulated, they base it on an average of major spot markets.
This prevents sudden wicks or fake trades from wiping out positions unfairly.
Your liquidation level is tied to this mark price, not the wild swings of a single exchange’s order book.
Risks and Rewards
Perpetual futures attract traders – especially day traders – because these instruments/markets never sleep.
You can trade Bitcoin with leverage around the clock, and even hedge a spot portfolio against sudden drops. The flexibility is great.
But the same features that make them appealing also make them dangerous. High leverage brings liquidation risk within striking distance.
A small move against you can erase your margin entirely.
Funding payments, while small at first, can eat into profits if you hold positions too long.
In normal markets, if you’re trading e-mini S&P 500 futures, each contract (around 50 shares of the underlying index) can have ~$10,000 in annual carrying costs for longs.
The lesson is simple: perpetual futures require discipline. Use stop-losses, respect leverage, and size positions realistically.
Pros & Cons
| Advantages | Risks |
| Trade 24/7 with no expiry | High volatility increases risk |
| Use leverage to amplify gains | Leverage also amplifies losses |
| Profit from rising and falling markets | Risk of liquidation |
| Funding rates are usually small | Can accumulate over time for large positions |
| Deep liquidity on major platforms | Requires understanding of margin mechanics |
Trading Strategies & Uses
Directional Bets
The most common way traders use Bitcoin perpetual futures is straightforward: making a directional bet.
If you think Bitcoin’s going up, you go long. If you believe it’s headed down, you go short.
With leverage, even small moves can become meaningful. If Bitcoin jumps 5 percent while you’re holding a 10x long, that’s a 50 percent gain on your margin.
The simplicity is what makes this strategy so popular.
But the opposite holds is also true. If you’re wrong, losses stack up just as quickly.
Hedging: Insurance for Holders
Hedging is where perpetual futures shine for long-term Bitcoin holders.
Let’s say you own BTC in a wallet, but you’re worried about a short-term drop. Instead of selling your coins, you can open a short perpetual.
If the market falls, your short gains offset your spot losses, giving you peace of mind without touching your core holdings. It’s like buying insurance against volatility, and it’s a strategy many institutions rely on to protect their balance sheets.
This is done in all sorts of markets.
Farmers short the commodities they produce or grow since they’re “long” the underlying market (e.g., the produce corn, milk, soybeans, etc.). Banks short Treasury futures to hedge duration risk.
Funding Rate Plays
The funding rate opens up a unique opportunity. Since longs and shorts pay each other every eight hours, traders can position themselves to earn from this flow.
For example, if the rate is positive, shorts receive payments from longs. Some traders take advantage by holding shorts just to collect the yield.
On the flip side, if the rate flips negative, longs get paid.
It’s not free money by any means. But for sharp traders, funding creates a steady stream of small gains.
Basis Trading: Playing the Gap
A more advanced strategy is basis trading, which looks at the price difference between perpetual futures and other markets, like spot or quarterly futures.
If perps are trading higher than spot, a trader might short the perpetual while holding the underlying asset, locking in the spread. If the perp trades at a discount, the reverse applies.
This strategy is less about predicting Bitcoin’s direction and more about capturing inefficiencies between markets. It requires more capital and discipline but can provide steady returns when done correctly.
It’s also important to be prepared for the basis widening and not overleveraging (see: LTCM disaster).
Platforms That Offer Them
Bitcoin perpetual futures are available on nearly every major crypto exchange. Bybit, OKX, Bitmex, and Kraken all provide deep liquidity and smooth trading. We have reviews on these brokers by clicking the associated hyperlink.
Each platform sets its own leverage limits (some as high as 100x or more), though most traders – prudently – stick to far less.
The important part isn’t chasing the biggest multiplier, but choosing a reliable exchange with fair pricing and solid risk management features.
Whether you’re a beginner testing small trades or an experienced trader running strategies, these platforms make perpetual futures accessible around the clock.
Conclusion
Bitcoin perpetual futures combine flexibility, leverage, and round-the-clock access. This makes them both “exciting” and dangerous.
They’re a way to speculate, hedge, or earn, but only if you respect the risks.
Always be sure to keep positions reasonable, use stop-losses, and always know your liquidation level.
Know what’s not acceptable and protect against that.
If you do choose to trade Bitcoin perpetual futures, approach them with a clear plan. Done right, they can add real value to your trading. Done carelessly, they’ll empty your account faster than you expect.