Ladder Options


Ladders have become an increasingly popular form of binary options trading in recent years. Investors essentially use ladder options to bet on which direction the market will move and by how much. This guide will explain what a ladder option is, how to get started trading, plus the pros and cons. We have also compiled a list of the top brokers for trading ladder options in 2026.
Ladder Options Brokers
Ladder Options Explained
Ladder options are a type of binary product first introduced by IG. They follow the same basic ‘yes or no’ principle as standard binary options but with some unique differences.
Firstly, a ladder option has multiple price levels, otherwise known as rungs, with most brokers offering up to five different tiers. Each rung normally has its own expiry time and prices can be above or below the current market price, or both. Each rung will also offer different returns with some levels offering over 500%.
Importantly, traders may satisfy some price levels but not others, depending on to what extent the market moves in their favour.
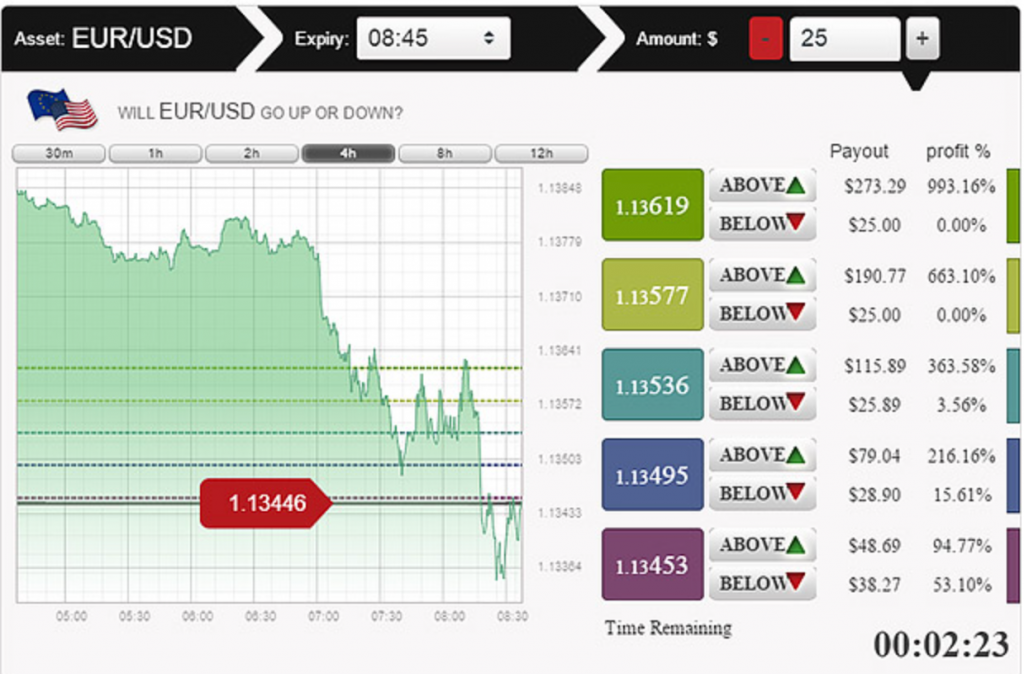
Example
Let’s say the GBP/USD price is 1.2260. A trader may choose to purchase ladder options with four price levels above the current market price and one rung below the current price:
- 1.2150 (below) – 1:00 expiry – 75% payout
- 1.2350 (above) – 0:30 expiry – 50% payout
- 1.2450 (above) – 1:30 expiry – 100% payout
- 1.2550 (above) – 2:oo expiry – 200% payout
- 1.2650 (above) – 2:30 expiry – 300% payout
Each price level has a different expiry time, with those closest to the current market price (1.2260) expiring first.
The price of the GBP/USD currency pair increases and goes on to satisfy three of the four price levels above the initial market price. So while the price level of 1.2650 and the price level below 1.2150 are not satisfied, the trader still makes a net profit.
Note, some binary options brokers call the ‘above’ and ‘below’ values ‘put’ and ‘call’.
Pros Of Ladder Options
- Potential for high returns
- More flexibility than standard binary options
- Popular in hedging strategies helping to manage risk in volatile markets
Cons Of Ladder Options
- Without a proper strategy, it is similar to gambling
- Higher payouts can be difficult to achieve due to the diminishing probabilities
- More complicated than standard binary options which may deter beginners
Strategies
Below we break down popular strategies for trading ladder options.
Momentum
This strategy involves using a historical average, such as a simple moving average, and comparing it to the current price level. If the current price level was 20% above the historical average, for example, this could indicate strong momentum and a bullish run. A trader would therefore want to set their price levels above the current price and may decide to move them further away from the market price if they feel particularly confident.
Hedging
Ladder options are popular with traders looking to manage risk in volatile markets. If a trader is unsure whether the market will move upwards or downwards, perhaps because there is no clear indication of whether the market is in overbought or oversold territory, they could place an equal number of price levels above and below the current market price. If a trader checks the payouts and returns make financial sense, they could offset potential losses.
Note, while this strategy is likely to reduce potential profit, it can help guard against erratic price movements in markets like cryptos.
Indicators
The right indicators complement the best ladder options strategies. Below we list several that could be of use.
Pivot Points
Pivot points are calculated by taking the average of the high, low and closing points of the previous trading day. They sometimes include other statistics such as the opening price or support and resistance levels.
They can be useful in identifying which direction the market is moving in and what the trend is. If the pivot point for the EUR/USD is 1.0392, for example, then a market price above this the following day may indicate a bullish (positive) trend. A market price below this could indicate a bearish (negative) trend.
Being able to predict the extent of trends is crucial for trading ladder options – it can help decide how many price levels to go for above the current market price and how many below.
Moving Averages
Moving averages look at the average price over a set time period. This is typically a period of 15, 30, 50, 100 or 200 days, but in theory, it could be any time period. The benefit of a moving average is that it reduces the impact of short-term fluctuations and allows the trader to see the broader picture.
It also helps to look at the change in the moving average itself – a rising moving average would suggest that the market is in an upward trend whereas a declining moving average would suggest the market is in a downward trend. As outlined above, being able to identify trends is key to a successful ladder options trading strategy.
Note, an exponential moving average (EMA) attaches more weight to recent days and is, therefore, more responsive to market events that have just occurred.
Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands are closely linked to moving averages. The upper and lower lines of a Bollinger Band are plotted two standard deviations away from a simple moving average. Plotting the band on a chart can help visualise the support and resistance levels for a particular asset. If the price moves towards the upper band, this may indicate that the asset is in overbought territory and the price may fall. Similarly, if the price moves towards the lower band, this may suggest it is in oversold territory and the price may rise.
Understanding whether an asset is in overbought or oversold territory can help traders pick out profitable ladder options.
Money Flow Index (MFI)
Like Bollinger Bands, the Money Flow Index (MFI) can be a useful indicator to show whether a market is in overbought or oversold territory. The MFI will have a value between 0 and 100. A value of 0 indicates that everybody that wants to trade the asset wants to sell it, whilst a value of 100 indicates the opposite – everyone that wants to trade the asset wants to buy it. A value of 50 would mean an equal number of buyers and sellers.
Importantly, if everybody wanted to sell the asset, this would suggest that the number of people wanting to sell has now been exhausted. In other words, the market is in oversold territory, which would indicate that a rise in the market price may follow. A value of 20 may indicate that the market is in oversold territory while a value of 80 could suggest that the market is in overbought territory.
How To Start Trading Ladder Options
Follow these straightforward steps to start trading ladder options:
1. Choose A Broker
Ladder options are a niche market. Not all brokers offer them so you may not have as much choice when it comes to finding a provider. Raceoption, for example, does provide ladder options.
Look at the potential payouts, expiry times and other contract conditions. Also compare premiums and other fees. Ideally, you also want a broker that allows you to deposit and withdraw from your account at no extra charge. Another key consideration is the trading platform – does it offer customisable charts? Is it available as a free mobile app?
2. Pick A Market
Ladder options can be used to speculate on a range of markets, from forex and stocks to commodities and cryptocurrencies. The key thing is to pick a market you have a good understanding of.
Traders should also choose a market that aligns with their risk tolerance. For example, risk-averse traders may want to avoid cryptos and exotic currency pairs.
3. Choose A Strategy
We have outlined some popular strategies for trading ladder options above. However, choose a strategy that suits your trading style and capacity. Short-term trading strategies, for example, often require lots of market research and monitoring, while longer-term approaches may be less time-intensive. Also decide whether you want to trade based on technical indicators or fundamental factors.

4. Expiry Times & Rungs
Once you are clear on your strategy, you can choose a ladder option with appropriate expiry times and price levels (rungs). Those using a hedging strategy may choose a ladder option with price levels above and below the current market price. On the other hand, those using a momentum strategy that have identified a positive trend may wish to buy a ladder option with price levels above the market price.
Remember that choosing ladder options with longer expiry times may mean you need to undertake fundamental analysis in addition to technical analysis, as the intrinsic value of the asset will have more of an impact.
Final Word On Trading Ladder Options
Ladders are an increasingly popular binary options product. Multiple price levels both above and below the market price of an asset, alongside various payouts, provide traders with a range of ways to make money. Trading ladder options is also appealing to investors interested in hedging strategies. Use this guide to get started and to find the best brokers for trading ladder options.
FAQs
What Factors Influence The Returns On A Ladder Option?
Potential payouts are influenced by the length of time between each rung, how close the current market price is to the specified levels, plus the volatility of the underlying market. See our list of brokers with the most competitive payouts to get started.
How Can Gamma Be Used When Trading Ladder Options?
Gamma measures the change in delta, which is a measure of the change in the price of an option relative to the value of the underlying asset. Gamma is essentially useful in determining the impact of price changes on the underlying asset. A high gamma indicates that the price of the underlying asset is at or close to the strike price, which means further price changes may have a large impact on the price of the option.
How Many Rungs/Price Levels Does A Ladder Option Have?
There is no set number of rungs for a ladder option so this can vary. With that said, most brokers and platforms offer up to five levels with different payouts and expiry times.
What Is The Difference Between A Ladder Option And A Binary Option?
Ladder options are a type of binary options contract. But where a standard binary option will contain a simple yes/no statement, ladder options contain multiple statements and strike prices relating to the same underlying asset.
