Risk Reversal

A risk reversal is a trading strategy that involves simultaneously buying an out-of-the-money call option and selling an out-of-the-money put option (or vice versa) on the same underlying asset to express a directional market view.
Risk reversal:
- Buy an out-of-the-money call option.
- Sell an out-of-the-money put option.
Also:
- Ensure the strike prices of both options are equidistant from the current price.
- Typically executed with little to no net premium cost.
Reverse risk reversal:
- Sell an out-of-the-money call option.
- Buy an out-of-the-money put option.
Top Brokers For Risk Reversal Strategies
A risk reversal is an options strategy often designed to hedge directional strategies.
For example, a long position will be hedged two-fold in a reverse risk reversal scenario:
1) By buying a put option, or an instrument that on its own rises in value when the underlying security decreases in value (holding time constant), and
2) By selling a call option, which is also bearish. You generate a net return when the company fails to move above its strike price by expiration. You collect a premium by selling the option at the outset of the transaction.
This works by helping to cap downside risk with the put option, but the price of the option cuts into the profit potential of the trade given it adds cost. Selling an option generates a premium, but the more it rises, the more likely it is that the option lands in-the-money (ITM) and the profit loss from the exercising of the option (the party on the other side of the trade) exceeds the premium procured. It also can directly cancel out profit generated from being long the underlying.
Likewise, a short position can be hedged by a normal risk reversal:
1) Buying a call option, or an instrument that on its own rises in value when the underlying security increases in value (holding time constant), and
2) Selling a put option, which is also bullish. You generate a net return when the company fails to move below its strike price by expiration. You collect a premium by selling the option.
Key Takeaways – Risk Reversal
- Directional Bet
- Combines a short position in out-of-the-money puts and a long position in out-of-the-money calls to express a bullish or bearish view.
- Cost Efficiency
- Can be set up with little to no net premium, which minimizes initial capital outlay.
- Volatility Play
- Profits from increased volatility.
- Makes it suitable for assets expected to move significantly in either direction.
- A risk reversal isn’t a bet on direction alone. You bet on direction, volatility skew, and market psychology simultaneously.
- Used correctly, it can be one of the most capital-efficient trade structures in derivatives trading.
Application
Risk reversals are commonly used to describe the implied trading biases among investors in currencies. It signals the difference in implied volatility between comparable call and put options.
The most important thing to understand about risk reversals is what the value of it – i.e., either positive or negative – signifies.
A positive risk reversal means that call options are more expensive than put options. This means that upside protection – for traders short the currency – is relatively expensive.
A negative risk reversal means that put options are more expensive than call options. This means that downside protection – for traders long the currency – is relatively expensive.
When there are material changes in the risk reversal this can indicate changing market expectations in the future direction of the underlying foreign exchange spot rate.
Therefore, risk reversals are typically used a signal of potential future trading activity. Accordingly, the use of risk reversals can be implemented as part of a broader strategy.
The Dynamics of the Risk Reversal
Positive risk reversal = Market is bullish on aggregate
Negative risk reversal = Market is bearish on aggregate
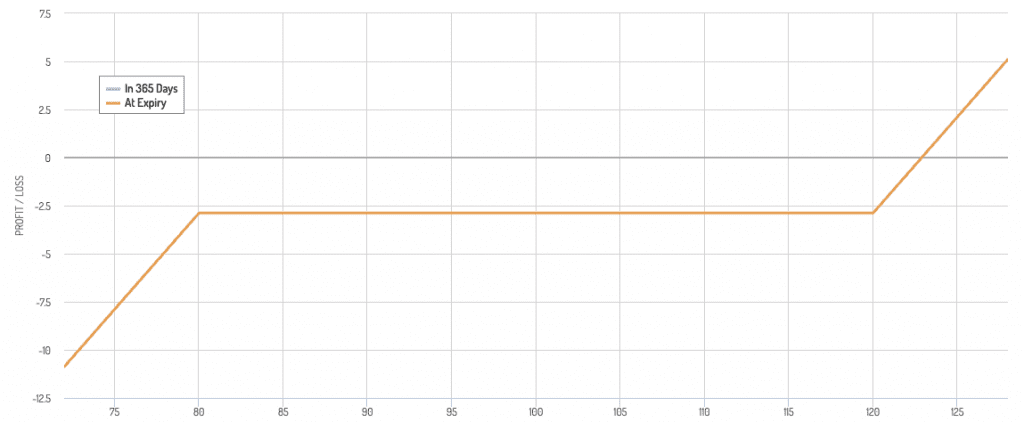
Bullish Risk Reversal Payoff Diagram
- Bullish: Sell an out-of-the-money put and buy an out-of-the-money call
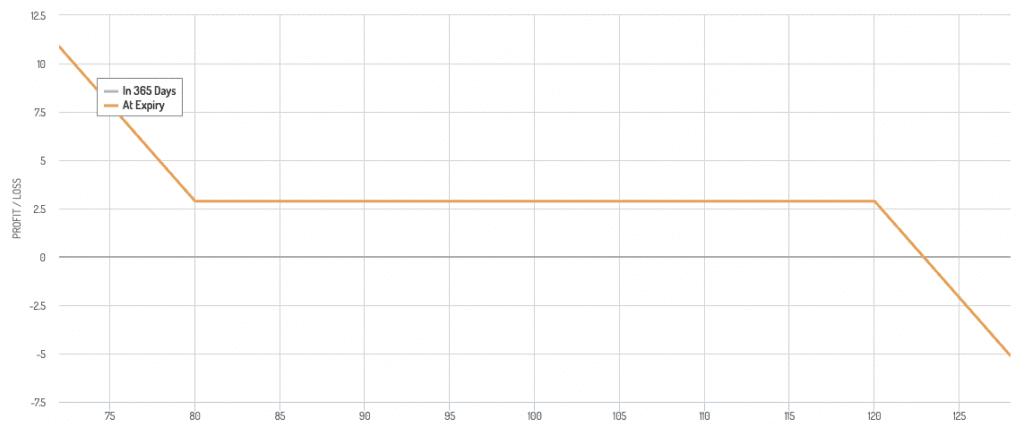
Bearish Risk Reversal Payoff Diagram
- Bearish: Sell an out-of-the-money call and buy an out-of-the-money put
You’re expressing directional bias while exploiting volatility skew, not delta alone.
If call options are more expensive (i.e., positive risk reversal), that signifies that there is more market demand for them. That means traders/investors are more bullish on that particular currency pair. That is, they expect it to increase in price.
On the same token, that can mean that there is more risk that a reversal could occur, as its name might suggest. Crowded trades are susceptible to amplified swings back in the other direction when there is a catalyst to set them off.
This is because you tend to see a large synchronization in the flow of orders relative to if the positioning in the market was more balanced.
Similarly, if put options are more expensive (i.e., negative risk reversal), that means higher market demand for them. Therefore, traders/investors are more bearish on that particular currency pair.
This also can set up a “squeeze” situation where a change in thinking on the market can cause a big shift back in the other direction. This can occur because either traders’ thought processes changed on the market causing the asset to reprice or else the pain of losing profits is too great to endure so they liquidate, exacerbating the move.
What Does the ‘Delta’ in a Risk Reversal Mean?
Delta in a risk reversal strategy measures the sensitivity of the position’s value to small changes in the underlying asset’s price.
For a risk reversal, delta combines the delta of the short put and the long call.
- Short Put: Typically has a positive delta, gaining value as the underlying price increases.
- Long Call: Also has a positive delta, gaining value as the underlying price increases.
The net delta reflects the overall directional exposure.
A positive net delta indicates a bullish bias, while a negative net delta indicates a bearish bias.
Why Are Risk Reversals Used to Describe Bullish or Bearish Bias in Currency Pairs?
Risk reversals indicate market sentiment by comparing the implied volatility of out-of-the-money calls and puts.
In currency pairs:
- Positive Risk Reversal – Implies higher demand for calls than puts, indicating a bullish bias.
- Negative Risk Reversal – Implies higher demand for puts than calls, indicating a bearish bias.
Traders use these to gauge market expectations and potential future movements. As such, it can provide insight into the underlying bullish or bearish bias for the currency pair.
High-Conviction Risk Reversals
Best when you expect a strong directional move and skew is favorable.
Bullish High-Conviction Setup
Here you sell a downside put with elevated implied volatility.
Buy an upside call where implied vol is cheaper.
Often done near event catalysts or macro inflection points.
Profit drivers
Risk
- You’re synthetically long the underlying below the put strike
- Requires strict sizing and margin discipline
Use when
- You want upside convexity but are comfortable owning the asset lower
- You believe downside tail risk is overstated
Bearish High-Conviction Setup
Here you want to sell an upside call with inflation implied vol.
Buy downside put where skew is cheap.
Works best when
- Rallies are crowded
- Call skew is extreme
- Downside hedging is underpriced
Low-Conviction Risk Reversals
Used when you have a mild directional bias but want favorable risk carry.
Characteristics
- Strikes placed further out of the money
- Often structured near zero cost
- Lower delta
- Lower margin stress
Profit drivers
- Time decay
- Skew persists
- Gentle spot drift
Why professionals use these
- Efficient expression of soft macro views
- Good carry without committing capital
- Useful for portfolio tilts rather than outright bets
Neutral Risk Reversals (Skew Trades)
These are not directional trades.
They’re volatility structure trades.
Structure
- Long one wing of skew
- Short the opposite wing
- Delta-neutralized
- If not delta-neutralized, then dynamically hedged
Profit drivers
- Skew compression or skew expansion
- Changes in tail hedging demand
- Flow-driven distortions
Examples
- Long puts short calls when crash insurance is crowded
- Long calls short puts when upside optionality is scarce
This is how desks trade other factors outside price.
Key Decision Matrix
| Market View | Preferred Structure | Primary Edge |
| Strong directional | Aggressive risk reversal | Delta + skew |
| Mild directional | Wide risk reversal | Carry + skew |
| No direction | Neutral risk reversal | Vol surface |
Common Mistakes
Some common mistakes when using risk reversals:
- Treating risk reversals as cheap calls or puts
- Ignoring margin exposure on the short leg
- Holding through regime shifts in skew
- Using them without a volatility thesis (delta + vega exposure)
When Risk Reversals Are Best
- Around macro events with asymmetric fear
- In commodities and FX where skew is structural
- They’re less used in equity markets
- When implied volatility misprices tail risk
- When funding costs make outright options inefficient



